Rawalpindi Board 2012
interPart1
Physics
Note:Pour possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct that circle in front that question with Marker or Pen ink. 'Lining or filling two or more circles 'will result in zero mat k in that question. Write the letter A, B. C or D in the column.(write correct "option) against each question also. If there k a contradiction in the bubble and hand written answer, bubble option will be considered correct.
- Distance
- As Fd =6, the dimension of coefficient of viscosity 17 is
- [ML-1T-1]
- [MLT-1]
- [ML-2T-1
- [ML
- |
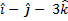 | =
| =
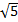
-
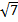
-
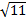
-
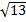
- If position vector and are in same direction then torque will be
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Same
- Negative
- During projectile motion, the horizontal component of velocity
- Changes with time
- becomes zero
- Remains constant
- increases with time
- The ratio of dimensions of K.E and power is
- 1 : 1
- T : 1
- 1 : 1-1
- M : T
- The rotational K.E of any hoop of radius 'r' is given by
- 1/2 2w2
- 1/2 2
- 1/2 r2w2
- None
- The dimension of angular acceleration is
- T-1
- T-2
- T-3
- LT-2
- Venturie -meter is a device used to measure
- Viscosity of fluid
- Density of fluid
- Pressure of fluid
- Speed of fluid
- In S.H, M the restoring force is directly proportional to
- Velocity
- Acceleration
- Displacement
- Time period
- The distance between a node and anti-node is
-

- Increase in velocity of sound in air for 1o C rise in temperature is
- 61m/sec
- 0m/sec
- 61m/sec
- 00m/sec
- When one mirror of a Michelson interferometer is moved a distance of 0.5mm, 2000 fringes are observed, the wave length of light used is
- 5000 nm
- 5000 °A
- 500 cm
- 2000 °A
- When light passes through a pinhole type opening, it seems to spread out. This phenomena is known as
- Dispersion
- Reflection
- Diffraction
- Polarization
- The speed of light in other material is always
- equal to C
- One is an example of a reversible process
- work done against friction
- heat produced by a current
- melting of ice
- see back effect
- Gas law PVr = constant is for
- iso-thermal process
- adiabatic process
- isobaric process
- isochoric process
Q2: Answer of 8/8 parts from questions No 2 & 3.While 6 parts from Q. No. 4
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which could serve as reasonable time standard
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity and acceleration of a car are
- Parallel
- Anti-parallel,
- If one of the rectangular components of a vector is not zero, can its magnitude be zero? Explain.
- Can a vector has a component greater than the vector's magnitude?
- At what point or points in its path does a projectile have its minimum and maximum speed?
- Calculate the work done in kilo joules in lifting a mass of 10 kg (at a steady velocity) through a vertical height of 10 m.
- A boy uses a catapult to throw a stone which accidentally smashes a green house window. List the possible energy
- Define Physics, steradian.
- Show that E = 2 is dimensionally consistent.
- What is the position vector?
- What is Impulse?
- Define elastic P.E and gravitational P.E.
Q3.
- Show that orbital angular momentum
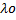 =
= 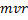
- Show that: 1 rad = 57.3o
- Why fog droplets appear to be suspended in air?
- Does frequency depend on amplitude for harmonic oscillator?
- How a chimney works best?
- Explain why sound travels faster in warm air than in cold air?
- What is the total distance traveled by an object moving with SHM in a time equal to its period, if amplitude is A.
- If a mass-spring system is hung vertically and set into oscillations, why does the motion eventually stop?
- A person is standing near a fast moving train. Is there any danger that he will fall towards it?
- Is it possible for two identical waves traveling in the same direction along a string to give rise to a stationary wave.
- How are beats useful in tuning musical instruments?
- A disc and a hoop start moving down from the top of an inclined plane at the same time. Which one will be moving faster on reaching the bottom?
Q4.
- Is it possible to convert internal energy into mechanical energy? Explain with an example.
- A heat engine is working between two temperatures 500 K and 300 K. Find its percentage efficiency.
- A telescope has objective lens of focal length 25 cm and eye piece of focal length 5 cm. Calculate the magnifying power of the telescope.
- Why the Polaroid sunglasses are better than ordinary sunglasses?
- State two conditions for detectable interference.
- Explain how a convex lens is used as a magnifier?
- The central spot is dark in Newton's Rings. Why?
- What is spectrometer? Write the names of its parts.
- State two of the postulates of kinetic theory of gases.
Answer any three questions.
Q5(A) State scalar product of two vectors. Write down any four properties of this product.
(B) A Truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a velocity of 21ms-1 collides with stationary car weighing 1000kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity.
Q6(A) Explain work done in gravitational field is independent of the path followed. Also define conservative field.
(B) A Gramophone record turntable accelerates from rest to an angular velocity of 45 rev/m in 1.60 sec. What is its average angular acceleration?
Q7.(A) Define molar specific heat at constant volume (Cv). Prove that: Cp — Cv = R
(B) Water flows through a hose. Whose internal diameter is 1 cm, at a speed of 1 m/sec. What should be the diameter of the nozzle, if the water is to emerge at 21 m/sec?
Q8.(A) What is Doppler's effect? Derive an expression for apparently changed frequency.
- When observer moves towards stationary source.
- When observer moves away from stationary source.
(B) A simple pendulum is 50 cm long. What will be its frequency of vibration at a place where g =9.13ms-2
Q9.(A) Define interference of light. Describe the construction and working of Michelson's interferometer.
(B) A telescope is made of an objective of focal length 20 cm and an eyepiece of 5.0 cm, both convex lenses. Find the angular magnification.