Bahawalpur BOARD 2013
PAPER CHEMISTRY PART-1
Time: 20 MM.
Marks: 17
Note: You have four choice for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. The choice which you think is correct; fill that circle in front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circles. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
- The number of moles of CO2 Which contain 8.0 g of oxygen:
- 0.25
- 0.50
- 1.0
- 1.50
- Empirical formula of Benzene is:
- CH2O
- CHO
- CH
- C3H3
- The comparative rates at which the solutes move in paper chromatography depends on:
- The size of paper
- Rf values of solution.
- Temperature of the experiment
- Size of chromatographic tank used
- In 1879, Plasma was identified by the scientist:
- John Dalton
- Chadwick
- William Crookes
- Soddy
- Ice occupies more space than liquid water:
- 9%
- 10%
- 19%
- 12%
- Which of the given is a Pseudo Solid:
- CaF2
- Glass
- NaCI
- All of these
- Quantum number value for 2p subshell are :
- n=2,
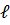 =1
=1
- n=1,
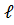 =2
=2
- n=1,
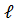 =0
=0
- n=2,
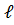 =0
=0
- 9.1095X
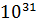 Kg
Kg
- 9.1095X
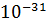 Kg
Kg
- 9.1095X
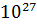 Kg
Kg
- 9.1095X
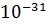 g
g
- The number of bonds in Nitrogen Molecule is:
- One sigma and one pie bond
- One sigma and two pie
- Three sigma only
- Two sigma and one pie
- Noble gases are highly stable and least reactive because:
- They are gases
- Their valence shell are complete
- They are present in zero group
- They are very safe
- Burning of coal is the example of:
- Non spontaneous Reaction
- Reversible Reaction
- spontaneous Reaction
- Irreversible Reaction
- For which system does the equilibrium constant, Kc has units of
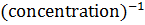
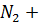 3
3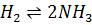
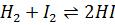
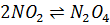
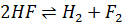
- The relationship between KP and Kc is given by:
- Kp = Kc
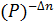
- Kc = Kp
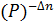
- Kp= Kc
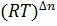
- Kc=Kp
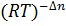
- The molal boiling point constant is the ratio of the elevation in boiling point to:
- Molarity
- Molality
- More fraction of solvent
- Mole Fraction of Solute
- If the Salt Bridge is not used between two half cells, then the voltage:
- Decrease Rapidly
- Decrease Slowly
- Does not change
- Drops to zero
- The electrolyte used in fuel cell is:
- Aqueous NaCI
- Molten NaCI
- KOH
- NaNO3
- A substance which promotes the activity of a catalyst is called:
- Activator
- Inhibition
- Retarder
- Autocatalyst
Subjective Part Time: 3:10 Hours Total marks 83
Note: It is compulsory to attempt (08) parts each from Q.NO. 2 and 3 while attempt 6 parts from Q.No. 4 and attempt any (03) questions from part-II .Write same question number and its part no, as given in the question paper.
Q.2.
- Actual yield is always lesser than Theoretical yield, why?
- N2 and CO have the same number of Electron, Proton and Neutron, how?
- What is a.m.u? Also give its value.
- State Distribution Law and distribution Coefficient K.
- Define sublimation with two examples.
- Give two applications of Dalton's Law of Partial Pressure?
- Explain Boyle's Law in the light of Kinetic Molecular Theory of Gases.
- Why Gases Deviate from their ideal behaviour?
- Evaporation causes cooling, why?
- Why Heat of syblimation of Iodine is very high?
- Ionic crystal are highly brittle, why?
- How Electrical conductivity of the metals decreases by increasing temperature?
Q.3.
- Why the positive rays are also called Canal Rays?
- Give Nuclear Reaction for the conversion of
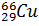 into
into 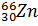 .
.
- Why the Rutherford's Atomic Model was unsatisfactory?
- Why the atoms of the elements other than Noble Gases combine with one another?
- State hund's Rule.
- Why no bound can have 100% Ionic Character?
- Why Bond order for He is zero?
- Define system and state Function.
- Define the term Buffer Capacity.
- Define a spontaneous Process and give an example.
- Why the value of Kw of water increases with the rise of temperature?
- Why Covalent Compounds react slowly than the Ionic Compounds.
Q.4.
- How do you justify that the greater quantity of Sodium Acetate Acid decreases the dissociation power of Acetic Acid so the pH increases.
- Define Kf and Kb for Reversible Reaction.
- Define Mole Fraction and Parts Per million.
- Give four rules for assigning of Oxidation number?
- Differentiate between a Cell and a battery.
- How the relative lowering of Vapour Pressure is independent of temperature?
- How the electrolysis of aqueous solution of sodium Nitrate gives 2 Gas at Cathode and O2 at Anode
- Give the name of four physical methods for the determination of rate of a reaction.
- How the increase of temperature increase the rate of reaction?
Q5. (A) Describe the measurement of Vapour Pressure by Manometric Method.
(B) NH3 gas can be prepared by heating together two solids NH4Cl and Ca(OH)2 If mixture containing 100 g each solid is heated then:
- Calculate the number of grams of NH3 Produced
- Calculate the excess grams of reagent unreacted
2NH4Cl + Ca(OH)2 —> CaC12 + 2NH3 + 2H2O Atomic masses: (Ca: 40 CI: 35.5 N=14)
Q6.(A) What is Hybridization? Explain Hybridization with an example.
(B) How Enthalpy of Combustion is determined with the help of a bomb calorimeter?
Q7. (A) What is Plasma? Write its three applications.
(b) Derive the equation for the radius of nth orbit of Hydrogen Atom using Bohr's Model.
Q8. (A) Write comprehensive notes on Alkaline Battery ( Non-rechargeable) and Nickel Cadmium cell (rechargeable).
(B) The solubility of CaF2 in water at 25°C, is found to be 2.05 x 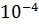 mol
mol 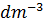 . What is the value of KSP at this temperature? (Atomic mass of Ca=40, Atomic Mass of F = 19)
. What is the value of KSP at this temperature? (Atomic mass of Ca=40, Atomic Mass of F = 19)
Q9. (A) Define the Colligative Properties and Explain the lowering of Vapour pressure is a colligative property.
(B) Explain Homogeneous and Heterogeneous catalysis with examples.
![]() mol
mol ![]() . What is the value of KSP at this temperature? (Atomic mass of Ca=40, Atomic Mass of F = 19)
. What is the value of KSP at this temperature? (Atomic mass of Ca=40, Atomic Mass of F = 19)