Bahawalpur BOARD 2013
PAPER CHEMISTRY PART-2
Time: 20 MM.
Marks: 17
Note: You have four choice for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. The choice which you think is correct; fill that circle in front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circles. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
- In the Mendeleev's Periodic Law the properties of elements are periodic function of their :
- Volume
- Densities
- Atomic Number
- Atomic Masses
- Plaster of Paris can be obtained from :
- Marble
- Bauxite
- Gypsum
- Limestone
- The chief ore of Aluminium is :
- Na3AlF6
- Al2O3 . 2H2O
- Al2O3
- A12O3.H2O
- Oxidation of NO in air produces :
- N2O
- N2O3
- N2O4
- N2O5
- The anhydride of HCLO4 is :
- ClO
- C1O2
- C1O3
- Cl2O7
- f - block elements are also called
- Non - Typical Transition Elements
- Outer Transition Elements
- Normal Transition Element
- Inner Transition Elements
- Linear Shape is associated with which set of Hybrid Orbitals
- SP
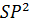
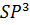
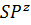
- Finyl acetylene combines with HCl to form.
- Polyacetylene
- Benzene
- Chloroprene
- Divinylacetylene
- During Nitration of Benzene the active agent is
- NO3
- NO2
- NO2
- HNO3
- To which one of the following is not a Nucleophile
- NH3
- H2O
- BF3
- H2S
- Phenol Reacts with CH3COCI to give :
- Acid
- Alcohol
- Aldehyde
- Ester
- Which of the following compounds will not give iodoform test on treatment with I2
- Acetaldehyde
- Acetone
- butanone
- Pentanone
- One of the following reagents will react with both Aldehydes and Ketones.
- Grignard's Reagent
- Tollen's Reagent
- Fehling's Reagent
- Benedict's Reagent
- The dipolar structure of Zwitter ion is also called
- Double Salt
- Health Salt
- Internal Salt
- External Salt
- Select the following Enzyme that brings about the Hydrolysis of fats
- Urease
- Maltase
- Zymase
- Lipase
- Ammonium Nitrate Fertilizer is not used for which crop:
- Cotton
- Wheat
- Sugarcane
- Paddy Rice
- Eco System is a smaller unit of
- lithosphere
- Hydrosphere
- Atmosphere
- Biosphere
Q2.
- Why Ionic Radii of positive ions are smaller than the size of their parent atoms?
- Why Alkali Metals give ionic hydrides?
- Write formulas of Asbestos and Natron?
- How Lime Mortor is prepared?
- Why 2 % Gypsim is added in the cement?
- P2O5 is a powerful dehydrating agent. Prove it giving two examples
- How aqua regia dissolved gold and platininum?
- Why is SO3 dissolved in H2SO4 and not in water?
- What is iodized Salt? Give its use.
- What are Non-Typical Transition Elements?
- How would you convert Ethyne into Acetaldehyde?
- Write down four uses of Methane.
Q3.
- Give four uses of Borax.
- How Boric Acid is prepared from Borax?
- Write a note on Tautomerism.
- Give two examples of Aromatic Compounds.
- Explain Wurtz - Fitting Reaction.
- How Benzene is prepared from n - haxane?
- Why Grignard's Reagents are so reactive?
- How will you convert Ethyl Bromide into Diethylamine?
- Lower alcohals are readily soluble in water. Explain.
- How will you prepare Ethanol from Molasses?
- How will you prepare an Amino acid by the Strecker Synthesis?
- How Acetic Acid is manufactured from Acetylene
Q4.
- Give reaction of Fehling's Solution with Foritialdehyde
- Why does Acetaldehyde pot give Canaizaro's Reaction?
- Write the reaction of Acetaldehyde with Hydrazine.
- Prepare Metaformaldebyde by using Formaldehyde?
- Define Macromolecules.Give two examples of Natural Macro Molecules
- What do you mean by Saponification Number?
- Write four essential qualities of Good Fertilizer.
- Write names of any two pulping processes used in paper industry.
- Name four component of Environment.
Q.5 (A) Discuss essential features of periods in Modern Periodic Table.
(B) Describe the manufacture of Sodium by Down's. Cell Diagram is not recquired
Q.6 (A) Explain the structure of Ethene on the basis of Hybridization.
(B) Discuss the Mechanism of base catalysed addition reactions of Carbonyl Compounds.
Q.7 (A) Describe Clemmensen and Wolf Kishner's Reduction for the preparation of Alkanes.
(B) What is a Grignard's Reagent? How is it prepared? Give its reactions with Water and Ammonia.
Q.8 (A) Discuss the structure of Benzene. How the open Chain structure ruled out?
(B) Define Amino Acids. What are essential and non essetial Amino Acids. Put a light on their nomenclature.
Q..9 (A) Explain the following terms with example.
- Ligands
- Co-ordination Sphere
- central Metal Atom
- Co-ordination Number
(B) Explain Acid Rain and give its effect on our environment.