BAHAWALPUR board 2013
PHYSICS
Inter Part— I
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Note:- THREE sections are in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc are not allowed in the examination hall.
- The capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor is:
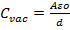
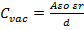
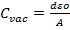
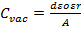
- The S.I unit of an Electric Flux is:
- Nm
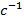
- Nm
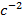
- N
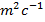
- N
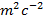
- Maximum power delivered by battery is:
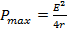
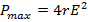
-
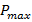 =VIT
=VIT
- Unlimited
- A shunted galvanometer is called:
- Ohmmeter
- Ammeter
- Voltmeter
- Potentiometer
- 1 NA
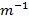
- 1 N
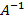 m
m
- 1 N
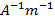
- 1NAm
- To construct a Step-down Transformer:
-
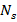 <
< 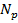
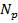 <
< 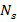
-
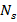 =
= 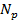
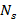 -
-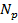 =1
=1
- The energy density of Magnetic Field B is given by:
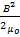
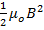
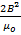
- 2
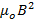
- Power Dissipation in a pure inductive or in a pure capacitance Circu us:
- Infinite
- Zero
- Minimum
- Maximum
- The impedance of a circuit containing inductor L and Resistance R us given by:
- LR

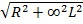
-
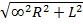
- The S.l unit of stress is same as that of:
- Momentum
- Pressure
- Force
- Length
- The number of diods in a bridge rectifier is:
- 5
- 4
- 3
- 2
- The potential difference across the depletion region of silicon is:
- 0.5 V
- 0.7 V
- 0.8V
- 0.11 V
- In Compton Scattering the Compton shift
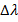 will be equal to Compton wavelength, if the scattering angle is:
will be equal to Compton wavelength, if the scattering angle is:
- Zero
-
-
-
- Platinum wire change to cherry red at:
-
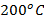
-
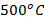
-
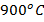
-
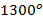 C
C
- For Halograph we use a beam of:
-
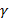 - rays
- rays
- X-rays
-
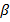 - rays
- rays
- Laser
- The fact that the super saturated vapours condense preferentially on ion is used to detect the radiation in the device is called:
- Nuclear Reactor
- G.M Counter
- Solid State Detector
- Wilson Cloud Chamber
- The particles which experience strong Nuclear Forces are known as:
- Lepton
- Photons
- Hadrons
- Neutrons
SUBJECTIVE PART
Q2 Attempt any 8 parts.
- If a point charge q of mass m is released in a non uniform electric field, will it make a rectilinear motion?
- Do electrons tend to go to region of high potential or of low potential?
- Give two properties of Electric Field Lines.
- With dielectric present between the charges how much electric force is increased or decreased. Give one example.
- Why the resistance of an ammeter should be very low?
- Describe the charge in the magnetic field inside a solenoid carrying a steady current I, if
- Length of the solenoid is double and the number of turns remains the same.
- The number of turns is doubled, but the length remains the same.
- What is Flux Density? Give its units.
- What is Lorentz Force?
- Give the back motor effect in Generators.
- How the eddy currents prevented to increase the efficiency of transformer?
- Does the induced emf always act to decrease the magnetic flux through a circuit?
- How would you position a flat loop of wire in a changing magnetic field so that there is no emf induced in the loop?
Q3. Attempt any 8 parts.
- A potential difference is applied across the ends of a copper wire. What is the effect on the drift velocity of electrons by increasing the potential Difference?
- Define Conductivity. Give its unit.
- Why terminal Potential difference of battery decrease when a current drawn from it is increased?
- In R-L series circuit will current lead or lag the voltage?
- A sinusoidal current has rms value of 10 A. What is its peak value?
- Define Choke.
- What is meant by Hysteresis Loss? How it is used in construction of transformer?
- What is meant by Para and diamagnetic substances? Give example for each.
- What is meant by Coercively?
- What is current gain of Transistor?
- What is net charge on n-type or p-type substance?
- Why ordinary silicon diodes do not emit light?
Q4. Attempt any 6 parts.
- What is Nuclear Fission? Explain it with equation.
- Why don't we observe a Compton Effect with visible light?
- Prove P =
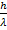
- Which has the lower energy quanta radio waves or x-rays?
- Find the speed of the electron in the first Bohr Orbit.
- The half life of
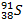 is 9.70 hours. Find its decay constant.
is 9.70 hours. Find its decay constant.
- Why are heavy Nuclei unstable?
- What do we mean by the term critical mass?
- Is energy conserved when an atom emits a photon of light?
SECTION-II
Q5:
- Drive expression for capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor. Also discuss effect of insertion of dielectric between plates of capacitor and hence define dielectric constant.
- A rectangular bar of iron is 2.0 cm by cross section and 40 cm long. Calculate its resistance if resistivity of iron is 11x
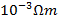 .
.
Q6:
- Define and explain Ampere’s Law. Find the magnetic field due to current carrying solenoid.
- The back emf of a motor is 120 volts when motor is running at 1680 revolution per minute. What is the back emf when the motor turns at 3360 revolutions per minute.
Q7:
- Define strain Energy. Find value of strain energy in a deformed material.
- A circuit has a inductance of
 H and resistance of 2000
H and resistance of 2000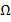 . A 50 HZ At is supplied to it. Calculate the reactance and impedance offered by the circuit.
. A 50 HZ At is supplied to it. Calculate the reactance and impedance offered by the circuit.
Q8:
- What is de Broglie Wavelength? By using Davisson and Germer Experiment show the wave nature of particle.
- Calculate the gain of no-inverting amplifier having resistance
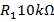 and resistance
and resistance 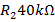 when
when 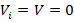
Q9:
- What is Laser? Describe its Principle and Operation?
- If 92
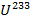 decays twice by
decays twice by 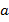 emission what is the resulting isotope?
emission what is the resulting isotope?