Inter (Part-II) Faisalabad Board 2013
Physics
Part I (Objective Type)
Time Allowed: 20 Minutes
Max. Marks: 17
Note: You have four choices for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. The choice which you think is correct; fill that circle in front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circles. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
Question #1
Circle the correct option i.e. A/B/C/D. Each part carries one mark.
- The electronic circuit which gives the inversion.
(A) X NOR gate
(B) OR gate
(C) AND gate
(D) NOT gate
- The potential barrier for Ge at room temperature is :
(A) 0.7 Volt
(B) 1 Volt
(C) 0.6 Volt
(D) 0.3 Volt
- The Compton shift in wavelength will be maximum when angle of scattering is :
(A) 90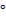
(B) 45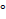
(C) 180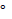
(D) 0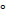
- An electric eye Operates because of:
(A) Compton effect
(B) Photo refraction
(C) Photo electric effect
(D) r-rays counter
- The energy of electron in the 4th orbit of Hydrogen atom is :
(A) -2.51ev
(B) -3.50 ev
(C) -13.6 ev
(D) -0.85ev
- IU (Unified mass scale ) is equal to:
(A) 880 Mev
(B) 931Mev
(C) 931ev
(D) 931 Kev
- Si Unit of absorbed dose is :
(A) Gray
(B) Roentgen
(C) Curie
(D) Rem
- If the magnitude of charge and distance between then is doubled then force will be :
(A) Doubled
(B) Halved
(C) Unaffected
(D) One forth
- SI Unit of electric Flux is :
(A) N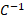
(B) N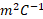
(C) Weber
(D) Tesla
- A wire of uniform area of cross section ‘A’ and Length ‘L’ is cut into two equal parts. The resistivity of each part is:
(A) Doubled
(B) Half
(C) remains the same
(D) Increase three times
- The value of e/m of neutron is :
(A) 1.75×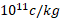
(B) 1.75×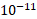 c/kg
c/kg
(C) 1.6×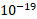 c/kg
c/kg
(D) Zero
- An electronic generator is based on the principle of:
(A) Faraday’s Law
(B) Lenz’s Law
(C) Ampere Law
(D) Gauss’s Law
- The Brightness of the spot of the CRO on the screen is controlled by :
(A) Cathode
(B) Anode
(C) Grid
(D) Plate
- Energy stored per unit volume in the inductor is :
(A)  L
L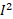
(B) 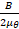
(C) 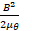
(D)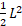 I
I
- SI Unit of impedance is :
(A) Henry
(B) Hertz
(C) Ampere
(D) Ohm
- In R-L-C series circuit, the current at resonance frequency is :
(A) Minimum
(B) Zero
(C) Maximum
(D) infinite
- Domains contain atoms nearly:
(A)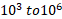
(B) 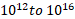
(C) 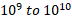
(D) 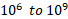
Inter (Part-II) Faisalabad Board 2013
Physics
Part II (Subjective)
Time Allowed: 2.10 Hours
Max. Marks: 83
Section I
Q2. Attempt any Eight short questions. (8×2=16)
- Electric lines of force never Cross. Why?
- If a point charge ‘q’ of mass m is released in a non -uniform electric field with field lined pointing in the same direction, will it make a rectilinear motion?
- What is strength of electric field inside a hollow charged sphere and why?
- How will capacitance of a parallel plate capacitor be affected if area of plates is doubled and separation between then is halved?
- How can you used a magnetic field to separate isotopes of a chemical element?
- Why the voltmeter should have very high resistance?
- What is Lorentz force?
- Do two long and parallel current carrying wires attract each other? Explain
- How does Lenz’s law explain conservation of energy during phenomenon of em induction?
- What are factors on which maximum value
 of emf induced across terminals of armature of an A.C. generator depend?
of emf induced across terminals of armature of an A.C. generator depend?
- Can an electric motor be used to drive an electric generator with the output from generator being used to operate motor?
- In a transformer, there is no transfer of charge from primary to secondary. How is then power transferred?
Q3. Attempt any Eight short questions. (8×2=16)
- A potential is applied across the ends of a copper wire. What is the effect of drift velocity of free electrons by increasing the potential difference?
- IS filament resistance lower or higher in a 500W, 220V bulb than in a 100W, 220 V Bulb?
- Name any four sources of current.
- What is meant by inductive reactance and capacitive reactance?
- A sinusoidal current has r.m.s value of 10A. What is the maximum or peak value?
- How does doubling the frequency affect the reactance of (a) an inductor (b) a capacitor?
- Distinguish Between amorphous and polymeric solids.
- Define stress and strain. Give Units of Both
- What is meant by hysteresis? How it is used in the construction of a transformer?
- What is the net charge on N-type or P-type substance?
- If
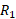 =10K Ohm and
=10K Ohm and 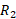 =100K Ohm. Find the gain of an inverting amplifier.
=100K Ohm. Find the gain of an inverting amplifier.
- What is the effect of depletion region of a PN junction when forward biased and when reverse biased?
Q4. Attempt any Six Short questions. (6×2=12)
- Why do not we observe Compton affect with visible light?
- Which has the lower energy Quanta? Radio waves or x rays.
- Give the two postulates of special theory of relativity.
- What do we mean when we say that atom is excited
- Give four uses of laser.
- What is difference between mass defect and binding energy?
- Define decay constant.
- What do you understand by background radiation? State two sources of these radiations.
- How can radioactivity help in the treatment of cancer?
Section - II
Attempt any three questions (8×3=24)
Question #5
(A) Define electric potential. Calculate the electric potential at a point due to a point charge. (2+2)
(B) A rectangular bar of iron is 2.0cm in cross-section and 40cm long. Calculate its resistance if the resistivity of iron is 11×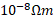 . (4)
. (4)
Question #6
(A) Derive an expression of force on a current carrying conductor placed in a uniform magnetic field. (4)
(B) Th Back emf in a motor is 120v when motor is turned at 1680 rev/min. What is the back emf when motor turns 3360 rev/min. (4)
Question #7
(A) What is energy band theory? Explain insulators and conductors on the basis of energy band theory. (4)
(B) Find the value of the current flowing through a capacitance 0.5µF when connected to a source of 150v at 50Hz. (4)
Question #8
(A) Describe de-Broglie hypothesis and explain is confirmation through Davisson and Germer experiment. (4)
(B) In a circuit, the transistor has collector current of 10mA and a base current of 40µA. What is the current gain of the transistor? (4)
Question #9
(A) Derive a relation for hydrogen emission spectrum and then explain the five results of atomic spectrum of hydrogen (4)
(B) The half-life of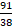 Sr is 9.7 hours. Find its decay constant. (4)
Sr is 9.7 hours. Find its decay constant. (4)
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
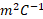
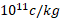
c/kg
c/kg
L
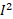
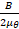
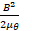
I
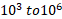
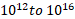
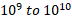
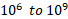
![]() . (4)
. (4)![]() Sr is 9.7 hours. Find its decay constant. (4)
Sr is 9.7 hours. Find its decay constant. (4)