(A) ![]()
(B) ![]()
(C) ![]()
(D) ![]()
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Chemistry (New Scheme)
Paper: I (Group-I)
Time: 20 Minutes
Marks: 17
OBJECTIVE
Note: Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct, fill that circle in front of that question with Marker or Pen ink in the answer-book. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
(A) Isotopes with even atomic masses are comparatively abundant.
(B) Isotopes with odd atomic masses are comparatively.
(C) Isotopes even atomic masses and even atomic number are comparatively abundant.
(D) Isotopes with even atomic masses and odd atomic numbers are comparatively abundant.
(A) 8 g of oxygen
(B) 16 g of oxygen
(C) 32 g of oxygen
(D) 24 g of oxygen
(A) non-volatile or thermally unstable
(B) volatile or thermally stable
(C) non-volatile or thermally stable
(D) volatile or thermally unstable
(A)
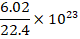
(B)
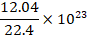
(C)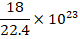
(D)
(A) Molecules of water in liquid state
(B) atoms of helium in gaseous state at high temperature
(C) Molecules of solid iodine
(D) molecules of hydrogen chloride gas.
(A) ionic crystals
(B) covalent crystals
(C) molecular crystals
(D) any type of crystals
(A) n = 2, ℓ = 1
(B) n = 1, ℓ = 2
(C) n = 1, ℓ = 0
(D) n = 2, ℓ = 0
(A) The nature of electrode
(B) The nature of discharge tube
(C) The nature of residual gas
(D) The temperature
(A) The ionization energy of A is high and electron affinity of B is low
(B) The ionization energy of A is low and electron affinity of B is high
(C) Both the ionization energy of A and electron affinity of B are high
(D) Both the ionization energy of A and electron affinity of B are low
(A) Energy is absorbed
(B) Forces of repulsion overcome forces of attraction
(C) Forces of attraction are equal to forces of repulsion
(D) Forces of attraction overcome forces of repulsion.
(A) qp = qv
(B) qp < qv
(C) qp > qv
(D)
(A) The value of Kp falls with rise in temperature
(B) The value of Kp falls with increase in pressure
(C) Adding V2O5 catalyst increases the equilibrium yield of sulphur trioxide
(D) The value Kp = Kc
(A) 25 times
(B) 75 times
(C) 55 times
(D) 65 times
(A) 5.85% solution of sodium chloride
(B) 18.00% solution of glucose
(C) 6.00% solution of urea
(D) all have the same boiling point
(A) Anode is negatively charged
(B) Reduction occurs at anode
(C) Cathode is positively charged
(D) Reduction occurs at cathode
(A) 5
(B) 6
(C) 3
(D) 7
(A) first order reaction
(B) second order reaction
(C) zero order reaction
(D) third order reaction
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Chemistry (New Scheme)
Paper: I (Group-I)
Time: 3:10 Hours
Marks: 83
SUBJECTIVE
(Section-I)
2. Write shore answers to any EIGHT (8) question: (16)
3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: (16)
4. Write short answers to SIX (6) question: (12)
(Section-II)
Note: Attempt any THREE question,
5. a) What is boiling point? What is the effect of external pressure on boiling point? Why the temperature of a liquid remains constant at boiling point although heat is continuously supplied? (4)
b) An ideal gas is enclosed in a container having volume 500 CM3 at S.T.P. Its mass comes out to be 0.72 g. What is the molar mass of this gas? (4)
6. a) Explain the molecular orbital structures of following molecules on the basis of the MOT:
(i) N2 (Nitrogen) (ii) O2 (Oxygen). (4)
b) State first law of thermodynamics. Prove that ∆E = qv- (4)
7. a) State Dalton’s Law of Partial Pressure, also give its three application.
b) Describe Millikan’s Oil Drop Method for the measurement of charge on electron. (4)
8. a) Describe the construction and the working of standard hydrogen electrode. (4)
b) What is the percentage ionization of acetic acid in a solution in which 0.1 moles of it has been dissolved per dm3 of the solution? (4)
9. a) Give three statements of Raoult’s law and also mention how Raoult’s law helps in determining the ideality of solution. (4)
b) What is Arrhenius equation? How it can be used to calculate activation energy of a reaction? (4)
(Section-III)
(Practical Part)
Note (i) Attempt ant THREE parts.
(ii) Write down standard solution, chemical equation with mole ratio, indicator with end point, procedure and supposed readings to calculation for Part A, B, and C. (1.1.1.1.1)
(iii) Write down material required, diagram and procedure for part D and E. (1,1,3)
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Chemistry (New Scheme)
Paper: I (Group-II)
Time: 20 Minutes
Marks: 17
OBJECTIVE
Note: Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct, fill that circle in front of that question with Marker or Pen ink in the answer-book. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
(A) Intermolecular hydrogen bonding
(B) Ion-dipole interaction
(C) Instantaneous dipole
(D) All of these
(A) 2.0 x 10-10 mole dm-3
(B) 1.4 x 10-5 mole dm-3
(C) 1.0 x 10-10 mole dm-3
(D) 4.0 x 10-20 mole dm-3
(A) Anisotropy
(B) Isomorphism
(C) Allotorpy
(D) Polymorphism
(A) Heat of reaction
(B) Heat of formation
(C) heat of neutralization
(D) Heat of combustion
(A) four
(B) Five
(C) Six
(D) Seven
(A) Trigonal planar
(B) linear
(C) V-shaped
(D) Tetrahedral
(A) First order reaction
(B) second order reaction
(C) Third order reaction
(D) Zero order reaction
(A) 1 dm3
(B) 1.8 dm3
(C) 200 cm3
(D) 900 cm3
(A) 14
(B) 12
(C) 6
(D) 13
(A) 8 g of oxygen
(B) 16 g of oxygen
(C) 32 g of oxygen
(D) 24 g of oxygen
(A) Independent of the wavelength
(B) depends on its wavelength
(C) Equal to square of its amplitude
(D) depends on its source
(A) Oxidation potential
(B) reduction potential
(C) Redox potential
(D) E.M.F of cell
(A) HF
(B) HBr
(C) HCℓ
(D) Hl
(A) Henderson
(B) Sorenson
(C) Goldstein
(D) Thomson
(A) 546
(B) 200
(C) 546K
(D) 273K
(A) Hydrogen
(B) Helium
(C) Oxygen
(D) Nitrogen
(A) I2
(B) I-
(C) I3
(D) I4
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Chemistry (New Scheme)
Paper: I (Group-I)
Time: 3:10 Hours
Marks: 83
SUBJECTIVE
(Section-1)
2. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: (16)
3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: (16)
4. Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions: (12)
(Section-II)
Note: Attempt any THREE question.
5. a) What are ionic solids?Give their properties in detail. 4
b) Calculate the number of grams of Aℓ2S3 which can be prepared by the reaction of 20g of Aℓ and 30g of sulphur. How much the non-limiting reactant is in excess? 4
(Atomic masses: Aℓ :27; S: 32)
6. a) Define electron affinity. Name the factors affecting it. How does it vary in the periodic table? 4
b) Define enthalpy of reaction. How is it measured by glass calorimeter? 4
7. a) Describe Lind’s method for the liquefaction of gases. 4
b) Describe Millikan’s Oil Drop Method for the measurement of charge on electron. 4
8. a) Describe the electrolysis of molten sodium chloride and a concentrated solution of sodium chloride. 4
b) N2 (g) , H2 (g) combine to give NH3 (g). The value of Kc in this reaction is 6.0 x 10-2 . Calculate the value of Kp for this reaction. 4
9. a) State and explain Raoult’s Law in three forms. 4
b) Explain Arrhenius equation. How does it help us to calculate the energy of activation of reaction? 4
Section-III)
(Practical Part)
Note (i) Attempt ant THREE parts.
(ii) Write down standard solution, chemical equation with mole ratio, indicator with
end point, procedure and supposed readings to calculation for Part A, B, and C.
(1.1.1.1.1)(iii) Write down material required, diagram and procedure for part D and E. (1, 1, 3)
A) 4 g of a mixture of Na2CO3 and Na2SO4 are dissolved in 500 cm3
Find out the %age composition of the mixture.( Molecular mass of Na2CO3 = 106) (5)B) 3 g of partially oxidized ferrous sulphate are dissolved in 100 cm3 Find out %age oxidation. (Molecular mass of FeSO4 = 152). (5)
C) 20 g of Na2S2O3 are dissolved in dm3 Fine out the %age of sulphur.
(Molecular mass of Na2S2O3 = 158) . (5)D) Identify Cu2+ and Cd2+ ions by paper chromatography. (5)