Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Physics (New Scheme)
Paper: I
(Group-I)
Time Allowed: 20 Minutes
Max.Marks:17
OBJECTIVE
Note: Four possible answers A,B,C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct, fill that circle in front of that question with Marker or Pen ink. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero. Mark in that question.
- The speed of sound in air depends upon:
(A) Temperature
(B) Humidity
(C) Density
(D) All of these
(A) Frequency
(B) Wavelength
(C) Intensity
(D) Speed
- The range of projectile is directly proportional to:
(A) Sin2 θ
(B) Sin 2θ
(C) Sin θ
(D) 2 Sin θ
- If a single convex lens is placed close to eye, then it is being used as:
(A) Telescope
(B) Microscope
(C) Magnifying glass
(D) None of these
- When a body moves in a circle, the angle between its linear velocity and angular velocity
 is:
is:
(A) 180°
(B) 90°
(C) 0°
(D) 45°
- The pressure exerted by a column of mercury 76 cm high and at 0°C is called:
(A) atmp
(B) 1 Nm-2
(C) 1 Pascal
(D) None of these
- The linear velocity of disc moving down an inclined plane is:
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
(A) k ̑
(B)1
(C)2
(D)0
- Distance between two consecutive nodes is:
(A) λ
(B) λ/4
(C) λ/2
(D) 2λ
- Write which of the following media can transmit both transverse and Longitudinal waves?
(A) Solid
(B) Liquid
(C) Gas
(D) Plasma
- The maximum drag force on falling sphere is 9.8 N, its weight is:
(A) 1 N
(B) 9.8 N
(C) 19.8 N
(D) 4.9 N
- A cricket ball is hit so that it travels straight up in air and it acquires 3Seconds to reach the maximum height. Its initial velocity is:
(A) 10 mS-1
(B) 15 mS-1
(C) 29.4 mS-1
(D) 12.2 mS-1
- One Geo-stationary satellite covers a longitude of:
(A) 270°
(B) 120°
(C) 90°
(D) 360°
- A stone is thrown up from the surface of the earth when it reach at maximum height, its K.E. is equal to:
(A) mgh
(B) 1/2 mv2
(C) Zero
(D) 2 mgh
- The frequency of second’s pendulum is:
(A) 1 Hz
(B) 2 Hz
(C) 0.5 Hz
(D) 5 Hz
- The efficiency of carnot engine depends upon:
(A)Sink temperature
(B)Source temperature
(C)Both source and sink temperature
(D) The working substance
- Solid angle subtended at the centre by a sphere is:
(A) 2π
(B) 4 π
(C) 6 π
(D) 8 π
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Physics (New Scheme)
Paper: II(Group-I)
Time : 3.10 Hours Marks:83
SUBJECTIVE
(Section-I)
2. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: 16
- Define Physics , Nuclear Physics.
- Define base Quantities, Derived Quantities.
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which could serve as reasonable time standard.
- Write the dimension of: (a) Velocity (b) Density
- Can a body rotate about its centre of gravity under the action of its weight?
- Name the three different condition that could make 1 x 2= 0.
- If all the component of the vectors 1 and 2 were reserved, how would this alter 1 x 2 =0 ?
- State Newton’s First and Second Law of Motion.
- Define elastic and inelastic collision.
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity and acceleration of a car are:
- Parallel (b) Anti-parallel
- Can the velocity of an object reserve the direction when acceleration is constant? If so, give an example.
- A person is standing near a fast moving train. Is there any danger that he will fall towards it?
3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: 16
- An object has one joule of potential energy. Explain what does it mean.
- A boy uses a catapult to throw a stone which accidentally smashes a greenhouse window. What energy changes are involved?
- What is geothermal energy? How it is generated?
- What is meant by centripetal force? Write down its formula.
- Show that orbital angular momentum L0 =mvr
- How is artificial gravity created?
- What happens to the length of simple pendulum, if its length is doubled?
- Can we realize an ideal simple pendulum?
- Define resonance and give an example of resonance.
- Is it possible for two identical waves travelling in the same direction along a string to give rise to stationary waves?
- Why does sound travel faster in solids than in gases?
- Can Doppler effect be applied to electromagnetic waves? Give an example.
4. Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions: 12
- What is polarization of light?
- How would you distinguish between unpolarized and plane polarized light?
- How would you manage to get more orders of spectra using a diffraction grating?
- Define total internal reflection.
- Why would it be advantageous to use blue light with a compound microscope?
- Derive Boyle’s law from Kinetic theory of gases.
- Give an example of a natural process that involves an increase in entropy.
- Why does the pressure of a gas in a car tyre increase when it is driven through some distance?
- State carnot theorem.
(Section-II)
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
5.a) Define rectangular components of a vector. How two vectors can be added By rectangular component methods? 5
b) Find angle of projection of a projectile for which its maximum height and horizontal range are equal. 3
6.a) Explain rotational K.E. Find the rotational K.E. of Disc. 5
b) A force (thrust) of 400 N is required to overcome road friction and air resistance in propelling an automobile At 80 km / hr. What power (kw) must the engine develop? 3
7.a) Derive the relation (a) acceleration. (b) instantaneous velocity, for the projection of a particle moving around a circle. 5
b) The frequency of note emitted by a stretched string is 300 Hz. What will be frequency of this note when the tension is increased by one-third without changing the length of the wire? 3
8.a) Discuss Young’s Double Slit Experiment. 5
b) An astronomical telescope having magnifying power of consist of two thin lenses 24 cm apart. Find the focal length of the lenses. 3
9.a) State and explain Torricelli’s theorem. 5
b) Calculate entropy change when 1 kg ice at 0°C melts into water 0°C latent heat of fusion of ice.
Lf=3.36 x 105 j/kg.
Section-III
(Practical Part)
A) Attempt any four questions. 8
- What is zero-error?
- What is the least count of screw gauge?
- What is difference between ‘g’ and ‘G’?
- Define centre of gravity.
- What is law of tension?
- What is correction?
- Define focal length of a lens.
- Define critical angle.
B) Write down the brief procedure to show experimentally that time period of simple pendulum is independent of amplitude. 3
OR
Write down the brief procedure to determine the focal length of a convex Lens by displacement method.
(a) What do you infer from the graph?
(b) Find the average acceleration from the graph. 4
Graph A
(Image)
OR
- What do you infer from the graph?
- Find the frequency from the graph corresponding to resonant length of the wire equal to 17.2 with same tension.
(Image)
Inter (Part-I)
Lahore Board 2013
Physics (New Scheme)
Paper: I
(Group-II)
Time Allowed: 20 Minutes
Max.Marks:17
OBJECTIVE
Note: Four possible answers A,B,C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct, fill that circle in front of that question with Marker or Pen ink. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero. Mark in that question.
- The percentage uncertainty in measurement of mass and velocity are 2% and 3%. The maximum uncertainty in the measurement of kinetic Energy is:
(A) 11%
(B) 8%
(C) 6%
(D) 1%
- The magnitudes of rectangular components of a vector are equal, if its angle with x-axsis is:
(A)0°
(B)30°
(C)45°
(D)90°
- The horizontal range of projectile at 30° with horizontal is the same as that at an angle of:
(A)45°
(B)60°
(C) 90°
(D) 120°
- Change in momentum is also called as:
(A)Force
(B)Acceleration
(C)Torque
(D)Impulse
- The force which can do not work on the body on which it acts is:
(A)Elastic force
(B)Friction force
(C)Centripetal force
(D)Gravitational force
- The angular momentum is given by:
(A) m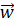
(B)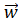 x
x 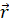
(C) 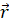 x
x 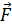
(D) 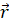 x
x 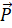
- Minimum number of communication satellites required to cover whole the earth is:
(A) 5
(B) 4
(C) 3
(D) 2
(A) 67.3°
(B) 57.3°
(C) 87.3°
(D) 45°
- The device used for the measurement of liquid flow is:
(A) Manometer
(B) Barometer
(C) Hydrometer
(D) Venturimeter
- The product of time period and frequency is:
(A) Zero
(B) 1
(C) π
(D) 2
- On increasing the tension, frequency of vibration of a string:
(A) Increase
(B)Decrease
(C)Remain constant
(D) First increase then decrease
- The wavelength of a fundamental mode of vibration of a closed pipe of length ‘ℓ’ is:
(A)ℓ/2
(B)ℓ
(C)2ℓ
(D) 4ℓ
- The speed of sound has maximum value in:
(A) Oxygen
(B)Air
(C)Hydrogen
(D)Helium
- The equation of Michelson’s Interferometer is:
(A) L=mλ/2
(B) L=mλ/2
(C) L=mλ
(D) L=2mλ
- The image formed by simple microscope is:
(A) Real and inverted
(B) Erect and virual
(C) Real and erect
(D) Invert and virtual
- Isothermal process is carried out at constant:
(A) Volume
(B) Pressure
(C) Energy
(D) Temperature
Boltzmann’s constant ‘k’ is equal to:
(A)R/NA
(B) 1/RNA
(C)NA/R
(D)RNA
Lahore Board 2013
Inter (Part-I)
Physics (New Scheme)
Paper: II
(Group-II)
Time : 3.10 Hours
Marks:83
SUBJECTIVE
(Section-I)
2. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: 16
- Name the several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which serve as reasonable time standard.
- Write the dimensions of pressure and density.
- Show that the equation s= vi+1/2 at2 is dimensionally correct.
- What are the three fundamental frontiers of fundamental sciences?
- If one of the rectangular components of a vector is not zero, can its magnitude be zero? Explain.
- How would the two vectors of the same magnitudes have to be oriented, if they were to be combined to give a vector of the same magnitude?
- Name the three different conditions that could make 1 X 2=0
- Why fog droplets appear to be suspended in air?
- An object is thrown vertically upward. Discuss the sign of acceleration due to gravity, relative to velocity, while the object is in air.
- Explain the circumstances in which velocity v and acceleration a of a car are: (a)Parallel (b) Perpendicular.
- Show that =∆/∆t.
- When a body is dropped from a height 4 m, calculate its velocity?
3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions: 16
- How you can get energy from tides?
- When a rocket reenters the atmosphere, its nose cone becomes very hot? Where does this heat energy come from?
- Prove that P=.
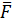 .
.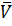
- State right hand rule to find the direction of angular displacement.
- Why banked tracks are needed for turns?
- When mud flies off the tyre of a moving bicycle, in what direction does it fly? Explain.
- What do you mean by phase?
- Write and explain electrical application of resonance.
- Does frequency depend on amplitude for harmonic oscillator?
- State the principle of superposition.
- How are beats useful in tuning musical instruments?
- Explain why does sound travel faster in warm air than in cold air.
4. Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions: 12
- How would you distinguish between unpolarized and plane polarized light?
- An oil film spreading over a wet footpath shows colours. Explain how does it happen.
- Can you obtain Newton’s rings with transmitted light? If yes, would the pattern be different from that obtained with reflected light?
- How the power is lost in optical fiber through dispersion? Explain.
- Find the magnifying power of a convex lens of 10 cm focal length.
- Does entropy of a system increase or decrease due to friction?
- Why adiabat is steeper than isotherm? Explain.
- What happens to the temperature of the room, when an ait-conditioner is left running on a table in the middle of a room?
- Derive Charles’ law from kinetic theory of gases.
(Section-II)
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
5.a) What is the projectile motion? Derive the relation for:
(a)Time of light (b) Maximum height for projectile. 5
- b) Find the angle between two forces of equal magnitude when the magnitude
of either of these forces. 3
6.a)What is centripetal force? Derive relation for it in terms of angular velocity. 1,4
b) A car of mass 800 kg travelling at 54 kmh-1 is brought to rest in 60 meters. Find the average retading on the car. 3
7.a)Show that the motion of projection of a body moving in a circle with constant speed is simple harmonic motion. 5
b)Two tuning forks exhibit beat at a beat frequency of 3Hz. The frequency of one of the fork is 256 Hz. Its frequency is then lowered by adding a bit of wax to one of its prongs. The two tuning forks then exhibit a beat frequency of 1 Hz.Determine the frequency of second tuning fork. 3
8.a) Define and explain simple microscope. 5
b) Yellow sodium light of wavelength 589 nm, emitted by a single source passes through two narrow slits 1.00 mm apart. The interference pattern is observed on a screen 225 cm away. How far apart are two adjacent bright fringes? 3
9.a) Define two specific heats of a gas and show that CP – CV =R 1,4
b) Water flows through hose whose internal diameter is 1 cm at speed of 1 mS-1.What should be the diameter of nozzle if the water is to emerge at 21 mS-1? 3
Section-III
(Practical Part)
A) Attempt any four questions. 8
- What is a least count of a screw gauge?
- What is meant by components of a vector?
- Define force and its S.I. unit.
- What do you mean by free fall?
- What is oscillatory motion?
- State Hook’s law.
- What is meant by resonance?
- What are stationary waves?
B) Write the brief procedure to show experimentally that time period of a simple pendulum is independent of mass. 4
OR
To show experimentally that area of a wire by screw gauge.
(a) Find the value of T2 AT X = 0.75 m.
(b)Find the value of ‘g’ from graph.
(image)
OR
(a)What information from graph?
(b)Find the slope.
(image)




x
x
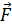
x