Rawalpindi board PHYSICS 2013
Interpart2
Physics
Note:Pour possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct that circle in front that question with Marker or Pen ink. 'Lining or filling two or more circles 'will result in zero mat k in that question. Write the letter A, B. C or D in the column.(write correct "option) against each question also. If there k a contradiction in the bubble and hand written answer, bubble option will be considered correct.
- Magnetism lags behind the magnetizing current, this phenomena is called:
- Coercively
- Hysteresis
- Retentively
- Saturation
- Electromagnetic waves emitted from an antenna are:
- Stationary
- Transverse
- Longitudinal
- X-rays
- The value of potential barrier for germanium is;
- 0.3 v
- 0.5 v
- 0.7 v
- 0.9v
- Photo diode can turn its current on and off in:
- Micro-sec
- Nano-sec
- Pico-sec
- Femto-sec
- 1 Kg mass will be equivalent to energy:
- 5x
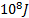
- 9 x
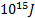
- 6x
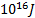
- 9 x
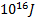
- When electron and positron are annihilated, the number of photons produced is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- Value of Rydberg's constant R, is:
- 1.0974 x
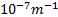
- 1.0974 x
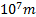
- 1.0974 x
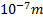
- 1.0974 x
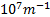
- Thyroid gland plays a major role in the distribution op
- Iodine
- Sodium
- Phosphorous
- Germanium
- Three up quarks combine to form a new particle, the charge number on this particle is:
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
- The minimum charge on an object cannot be less than:
- 9x
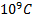
- 1.6 x
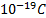
- 1.6x
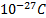
- 9.1 x
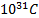
- If the distance between two charged bodies is halved, the force:
- One fourth
- Half
- Double
- Four times
- Electromotive force is most closely related to:
- Electric field
- Potential difference
- Potential energy
- Magnetic field
- The unit of magnetic flux is:
- Weber
- Tesla
- Henry
- Coulomb
- The convert galvanometer into ammeter the parallel shunt resistance R, is equal to:
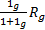
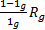
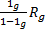
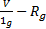
- The principle of a.c generator is:
- Mutual induction
- Self induction
- Lenz's law
- Electromagnetic field
- Eddy currents are produced in a material when it is:
- Heated
- Placed in an electric field
- Placed in a uniform magnetic field
- Placed in time varying magnetic field
- At resonance frequency, the current in RLC series circuit is:
- Infinity
- Maximum
- Minimum
- Zero
Section II
Q.2 Attempt any EIGHT short questions.
- Define and give the S.1 units of electric potential.
- Show that
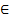 and
and 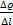 have the same units.
have the same units.
- Differentiate between motor and generator.
- Why the resistance of an ammeter should be very low?
- How a capacitor is charged and discharged? Draw its R-C circuit?
- Suppose you follow an electric field line due to a positive point charge. Does electric field increase or decrease? Also what about potential?
- Why does the picture on a T.V screen distorted. When a magnet is brought near the screen?
- Flow can a cun.ent loop be used to determine the presence of a magnetic field in a region of space?
- How can you use magnetic filed to separate isotopes of chemical element?
- Does the induced emf always act to decrease the magnetic flux through the circuit?
- Does the induce emf in a circuit depends on the resistance of the circuit? Does the induced current depends on the resistance of the circuit?
- Electrons always move towards high potential. Explain why?
Q.3 Attempt any EIGHT short questions.
- What is wheat stone bridge and draw its figure?
- What is meant by A.M and F.M?
- Why glass is known as solid liquid?
- How can a rheostat be used as potential divider?
- Why ordinary silicon dioxide does not emit light?
- Explain brief the conductors on the basis of energy band theory.
- Explain why the terminal potential difference of a battery decreases when the current drawn from it is increased?
- Differentiate between ferromagnetic and diamagnetic substances.
- When 10v are applied on an A.C circuit the current flowing in it is 100 mA? Find its impendence.
- How the reception of a particular radio station is sleeted on your radio set?
- What is the effect of forward and reverse baising of a diode on the width of delpletion region?
- Define input resistance and out-put resistance of an operational amplifier?
Q.4 Attempt any SIX short questions.
- Give two postulates of special theory of relativity.
- Define excitation energy and ionization energy.
- What is the radioactive tracer?
- What do you mean by critical mass and critical volume?
- Give two advantages of laser over ordinary light.
- Describe principle of operation of solid state dector
- Is it possible to create a single electron from energy? Explain.
- When does light behave as a wave and when does it behave as a particle?
- Protons and neutrons are formed by what types of quarks'? Show by diagram.
Attempt any THREE questions.
Q5:(A) Define electric potential Also derive an equation for electric potential at a point due to a point charge.
(B) The potential difference between the terminals of a battery in open circuit is 2.2v when it is connected across a resistance of 5.0, the potential falls to 1.8 v. Calculate the current and internal resistance of battery.
Q6:(A) Define motional emf and derive a relation for it
(B) A solenoid 15cm long has 300 turns of wire. A current of 5 ampere flows through it what is the magnitude of magnetic field inside the solenoid?
Q7: (A) Describe R.L.C series A.C circuit. Write down its properties and find the relation for resonance frequency.
(B) A 1.25 cm diameter cylinder is subjected to a load of 2500 Kg. Calculate the stress on the bar in mega Pascal’s.
Q8: (A) Write down postulates and results of special theory of relativity. What is NAVSTAR navigation system?
(B) Calculate the output of the op-amp shown in figure.
Q9: (A) Define isotopes. Write a note on mass spectrograph.
(B) Calculate the longest Wave length of radiation for Paschen series.