(A) f=2π![]()
(B) f= ![]()
![]()
(C) f=![]()
![]()
(D) f=2π![]()
Inter (Part-I)
Gujranwala Board 2014
Physics (New Scheme)
Paper : I
(Objective)
Time: 20 Minutes
Marks: 17
Note: You have four choices for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. The choice which you think is correct, fill that circle in front of that question number with marker or pen on the answer book provided. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question. Attempt as many questions as given in objective type question paper and leave others blank.
(A) 16 J
(B) 8 J
(C)32 J
(C)2 J
(A) 10 m
(B) 10-10 m
(C) 10-2 m
(D) 10 cm
(A) long distance
(B) short distance
(C) very long distance
(D) infinite distance
(A) 332 ms-1
(B) 332 cms-1
(C) 222 ms-1
(D) zero
(A) f=2π
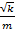
(B) f=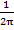
(C) f=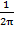
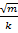
(D) f=2π
(A)
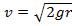
(B)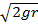
(C)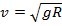
(D) V= V=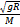
(A) 57.30
(B) 5730
(C) 57300
(D) 5.730
(A) force
(B) acceleration
(C) instantaneous acceleration
(D) power
(A) area
(B) volume
(C) length
(D) velocity
(A) hydrometer
(B) barometer
(C) galvanometer
(D) sphygmomanometer
(A) maximum
(B) infinite
(C) zero
(D) variable
(A) 300
(B) 450
(C) 150
(D) 00
(A) 2ℓ
(B) ℓ/2
(C) 4ℓ
(D) ℓ
(A)π rad
(B) rad
(C) rad
(D)2 π rad
(A) iˆ
(B) jˆ
(C) kˆ
(D) -iˆ
(A) power
(B) torque
(C) pressure
(D) force
(A) energy
(B) force
(C) momentum
(D) power
Inter (Part-I) Gujranwala Board 2014
Physics (New Scheme) Paper : I (Subjective)
Time: 3.10 Hours
Marks: 83
Note: Section I and II are compulsory. Attempt any three (3) questions from Section II.
(Section-I)
2. Write short answers to any EIGHT questions: (2x8=16)
3. Write short answers to any EIGHT questions: (2x8=16)
4. Write short answers to any SIX questions: (2x6=12)
(Section-II)
5.(a) Describe elastic collision in one dimension. Show that Relative velocities before collisions = Relative velocities after collisions. (5)
(b) Find the angle between the two vectors:
A= 5 i + j and B = 2i + 4j 36.(a) Define absolute potential energy. Derive its mathematical expression. 1,4
(b) The earth rotates on its axis once a day. Suppose, by some process the earth contracts so that its radius is only half as large at present. How fast will it be rotating then? (3)
(For sphere I = 2/5 MR2)7.(a) What is simple pendulum? Show that motion of simple pendulum is simple harmonic motion. Also derive the relation for its time period. 1,4
(b) A church organ consists of pipes each open at one end of different lengths. The minimum length is 30 mm and the longest is 4 m. Calculate the frequency range of the fundamental notes. ( speed of sound = 340 ms-1) (3)
8.(a) What is compound microscope? Calculate its magnifying power.
(b) A light is incident normally on a grating which has 2500 lines per centimeter. Compute the wavelength of a spectral line for which the deviation in second order is 15.00. (3)
(b) An airplane wing is designed so that the speed of the air across the top of the wing is 450 ms-1, the speed of air below the wing is 410 ms-1, What is the pressure difference between the top and bottom of the wings? Density of air = 1.29 kgm-3 (3)
(Section-III)
(Practical)
10.(a) Write answers to any four parts: 4x2=8
(b) Write down the brief procedure to find experimentally the refractive index of the material of a prism by critical angle method. (3)
OR
Write down the brief procedure to find experimentally the unknown weight of body by the method of vector addition of forces.
(c) Answer the following questions on the basis of graph below: (4)
(i) What is the relation between F and x.
(ii) Find the value of the spring constant.
OR
(i) What do you infer from the graph?
(ii) Find the frequency when = 0.04 cm-1