RAWALPINDI BOARD 2014
PHYSICS
PART-I
Time: 20 Min.
(Objective Part)
Marks: 17
Note: You have four choice for each objective type question as A,B,C and D. The choke which you think is correct; fill that circle in front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circles. Cutting or Ming two or more circles Will result in zero mark in that question.
- For working of heat engine, there must be:
(a) scource
(b) A sink
(c) Either of these
(d) Both of these
- The curve representing an adiabatic process is called:
(a) An adiabat
(b) An isotherm
(c) Both of these
(d) None oftese.
- The unit of work in base unit is:
(a) Kgm-1 sec-2
(b) Kgm sec2
(c) Kgm2 sec2
(d) Kgm-1 sec-1
- The firstcondition of equilibrium implies that:
(a) Σƒ = 0
(b) Σƒx = 0
(c) Σƒy = 0
(d) Σƒx = Σƒy
- The velocity of a projectile is maximum.
(a) at the highest point
(b) at point of launching arid just before striking the ground
(c) at half of the height
(d) after striking the ground
- Impulse can be defined as:
(a) 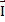 =
= 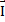 x
x 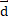
(b) 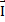 =
= 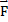 x t
x t
(c) 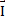 =
= 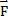 x
x 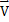
(d) 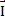 =
= 
- Biomass is a potential source of:
(a) Renewable energy
(b) Non-Renewabie energy
(c) Both
(d) Tidal energy
- Close orbiting satellites orbit the earth at a height of about:
(a) 400 km
(b) 4000 km
(c) 400 m
(d) 40 cm
- The force and torque are analogous to:
(a) Velocity
(b) Mass and weight
(c) Moment of inertia
(d) Each other
- Relation between escape elocity "Vesc„ and orbital velocity "V0" is:
(a) Vesc = ½ Vo
(b) Vesc = 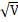 o
o
(c) Vesc = Vo
(d) Vesc = 2Vo
- A 6.0 metre high tank is full of water. A hole appears at its middle. What is the speed of efflux.
(a) 7,66ms-1
(b) 5.66ms-1
(c) 6.66ms-1
(d) 8.66ms-1
- When a particle is moving along a circular path, its projection along the diameter executes:
(a) Linear motion
(b) Vibratory motion
(c) Rotatory motion
(d) SHM
- With increase of temperature speed of sound:
(a) Remains constant
(b) Becomes zero
(c) Decreases
(d) Increases
- Two tuning forks of frequencies 243Hz 240Hz and are sounded together, the number of beats per second is:
(a) Zero
(b) 4
(c) 3
(d) 2
- The distance between two consecutive nodes and anti nodes is:
(a) λ
(b) 
(c) 2λ
(d) 
- In Young's double slit experiment, the position of dark fringes is given by
(a) Ym = mλL/d
(b) Ym = mλL/L
(c) Ym = ( m + ½ ) λL/d
(d) Ym = ( m + ½ ) λd/L
- The final image seen through eye piece in telescope is:
(a) Real, enlarge and inverted
(b) Virtual, enlarge and erect
(c) Virtual, enlarge and inverted
(d) Real, enlarge and erect
RAWALPINDI BOARD 2014
PHYSICS
PART-I
Time: 3:10 Hours
(Subjective Part)
Marks: 83
Section II
2. Attempt any EIGHT short questions. (8 X 2 = 16)
- Name several repetitive phenomenon °caning in nature which could serve as reasonable time standard.
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity and acceleration of a car are
(i) parallel
(ii) Anti-parallel.
- If one of the rectangular components of a vector is not zero, can its magnitude be zero? Explain.
- Can a vector has a component greater than the vector's magnitude?
- At what point or points in its path does a projectile have its minimum and maximum speed?
- Calculate the work done in kilo joules in lifting a mass of 10kg (at a steady velocity) through a vertical height of 10m.
- A boy uses a catapult to throw a stone which accidentally smashes a green house window. List the possible energy changes.
- Define Physics, steradian,
- Show that E= mc2 is dimensionally consistent.
- What is the position vector?
- What is Impulse?
- Define elastic P.E and gravitational P.E.
3. Attempt any EIGHT short questions. (8 x 2 16)
- Show that orbital angular momentum λo = mvr.
- Show that : 1 rand = 57.3°
- by fog droplets appear to be suspended in air?
- Does frequency depend on amplitude for harmonic oscillator?
- How a chimney works best'?
- Explain by sound travels faster in are air than in cold air''?
- What is the total distance travelled by an object moving with SHM in a time equal to its period, if-amplitude is A.
- If a mass-spring system is hung vertically and set into oscillation, why does the motion eventually stop?
- A person is standing near a fast moving train. Is there any danger that he will fall towards is?
- Is it possible for two identical waves travelling in the same direction along a string to give rise to a stationary wave.
- How are beats useful in tuning musical instruments?
- A disc and a hoop start moving down from the top of an inclined plane at the same time. Which one will be moving faster on reaching the bottom?
4. Attempt any SIX short questions. (6 x 2 = 12)
- Is it possible to convert internal energy into mechanical energy?Explain with an example.
- A heat engine is working between two temperatures 500 K and 300 K.Find its percentage efficiency.
- A telescope has objective lens of focal length 25cm and eye piece of focal length 5cm. Calculate the magnifying power of the telescope.
- Why the Polaroid sunglasses are better than ordinary sunglasses?
- State two conditions for detectable inference.
- Explain how a convex lens is used as a magnifier?
- The central spot is dark in Newton's Rings why?
- What is spectrometer? Write down the names of its parts.
- State two of the postulates of kinetic theory of gases,
SECTION-III
Attempt any THREE questions. (8 x 3 = 24)
5. (a) State scalar product of two vectors. Write down any four properties of this product.
(b) A Truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a velocity of 21ms-1 collides with stationary car weighing 1000kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity.
8. (a) Explain work done in gravitational field is independent of the path followed. Also define conservative field.
(b) A Gramophone record turntable accelerates from rest to an angular velocity of 45 rev/m in 1.60 sec. what is its average angular acceleration?
7. (a) Define molar specific heat at constant volume (Cv). Prove that:Cp - Cv = R.
(b) Water flows through a hose, whose internal diameter is 1 cm, at a speed of 1 m/sec. What should be the diameter of the nozzle, if the water is to emerge at 21 m/sec?
8. (a) What is Doppler's effect? Derive a expression for apparently changed frequency.
- When the observe moves towards the stationary sources.
- When the observe moves away from the stationary sources.
(b) A simple pendulum is 50 cm long. What will be its frequency of vibration at a place where g = 9.8ms-2
9. (a) Define interference of light. Describe the construction and working of Michelson’s interferometer:
(b) A telescope is made of an objective of focal length 20 cm and an eyepiece of 5.0 cm, both convex lenses. Find the angular magnification.
![]() =
= ![]() x
x ![]()
![]() =
= ![]() x t
x t![]() =
= ![]() x
x ![]()
![]() =
= ![]()
=
x
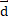
=
x t
=
x
=
o