Statistics
Paper I (Objective Type)
Inter - A – 2016
Old Pattern
Time Allowed : 20 Minutes
Inter (Part - I )
Maximum Marks: 17
Session ( 2012 - 14 )(2013 - 15)(2014 - 16)
Note: Four Possible choices A,B,C,D. to each question are given which choice is correct fill the circle front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circle. Cutting or filling two or more circle will result in zero mark in question.
Question#1
- The number of observations falling in a particular class is called:
(A) Tally Mark
(B) Class Frequency
(C) Class
(D) None of these
- The process of arranging data Into rows and columns is called :
(A) Presentation
(B) Tabulation
(C') Classification a
(D) Arranging Data
- The word “Statistics ' is the plural of :
(A) Sample
(B) Statistic
(C) Variable
(D) Parameter
- Which of the following Average can have more than one value:
(A) A.M.
(B) H.M.
(C) Mode
(D) Median
- The Variance of 7 , 7 , 7 is equal In
(A) 7
(B) 49
(C) 0
(D) 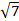
- The first moment about mean is equal to:
(A) 1
(B) 0
(C) Variance
(D) S.D.
- Sum of deviations of observed value from their mean is :
(A) One
(B) Zero
(C) <
(D) > 0
- The mean deviation is least when deviation are taken from :
(A) Mean
(B) Median
(C) Origin
(D) Mode
- The set of all possible outcomes of a Random Experiment is called :
(A) Null Set
(B) Sample Space
(C) Empty Set
(D) None of these
- When all the values are of equal Importance, then Index Numbers are called:
(A) Simple Index
(D) Weighted Index
(C) Unweighted Index
(D) Cost of Living Index
- In a fixed base method, which period is always taken as 100:
(A) Preceding Period
(B) Base Period
(C) Following Period
(D) Current Period
- Probability of an event always lies between
(A) - 1 and 0
(B) - 1 and 1
(C) 0and 1
(D) 1 and 2
- For a Binomial Distribution with n = 5, P = 0.2 , P( x = -2) is equal to:
(A) 0
(H) < 0
(C) > 0
(D) 1
- In a Hypergeometric Experiment, the successive trials are:
(A) Independent
(B) Dependent
(C) Infinite
(D) Exhaustive
- A Random Variable may be discrete or:
(A) Experimental
(B) Continuous
(C) Functional
(D) None of these
- Parameters of the Binomial Distribution are:
(A) n and q
(B) n and p
(C) p and q
(D) n and N
- Sum of all Probabilities is equal to :
(A) -1
(B) 1
(C) 0
(D) 2
Statistics (Subjective Type)
Inter - A – 2016
Inter (Part - I )
Time = 3:10 Hours
Total Marks: 83
Note:It is compulsory to attempt (8-8)parts each from Q.No.2 and 3 while attempt any 6 partsfrom Q.No.4 and attempt any (03) questions from part- II while from section -III (practical part) (03)parts should be attempted Write same question No. and its part No as given in the question paper.
(Section - I)
2. Attempt any 8 questions (2x8=16)
- Name the two sources of Secondary Data.
- Differentiate between Parameter and Statistic.
- Define Combined Mean.
- Define the term Mode.
- If I= 19.5 . h = 10 ,f = 15 ,n = 60 and C = 28 then find Median.
- If mean = 30. 5 , Median = 12 . 3 then find Mode by using the Empirical Relationship.
- Give the two properties of Arithmetic Mean,
- Define Link Relatives.
- What is C.P.I.?
- What in Unweighted Index Number"
- Describe the Chain Base Method.
- Given Laspeyre's Price Index Number = 105. And Paasche's Price Index Number = 110,
- Compute Fisher Ideal Price Index Number.
2. Attempt any 8 questions (2x8=16)
- Define Class Mark,
- Define Frequency Polygon.
- If Q1 = 50 , Q2 = 60 and Q3 = 75 then find Bowley's Coefficient of Skewness.
- If Var (x) = 5,Var (y ) = 2 then find Var (2x + y )
- Define Relative Dispersion.
- Define Quartile Deviation.
- Write two properties of Standard Deviation.
- Define Random Experiment.
- Define Equally Likely Events.
- Define Sure Event.
- Define Independent Events.
- Write down Karl Pearson's 1st formula of Skewness.
2. Attempt any 6 questions (2x6=12)
- In a Binomial Distribution n = 10, I' = 0. 3find Mean and Variance.
- Write down the properties of a Discrete Probability Distribution.
- If E (x ) = 5 and E (x 2) = 50 find Var ( x )
- Define Discrete Random Variable.
- Write down the formula of F.( x ) and E ( x2)
- What is Hypergeometric Random Variable?
- In a Binomial Distribution n = 3, P = 1/2find P( x ≤ 2)
- Define Distribution Function.
- Define Hypergeometric Experiment
Section - II
Question#5
(a) Find the H.M. for the data given below. 04
| x |
10
|
12
|
14
|
16
|
18
|
20
|
|
f
|
1
|
3
|
7
|
12
|
8
|
1
|
(b) Compute Mode from the following Data. 04
|
Clauses
|
2-4
|
4-6
|
6-8
|
8-10
|
10-12
|
|
Frequency
|
4
|
10
|
15
|
12
|
3
|
Question#5
(a) Find Quartile Deviation and Coefficient of Q.D. from the following observations :04
10, 12, 15, 25. 28, 35, 42, 20, 12, 5
(b) Calculate S.D., Variance and C.V. from the data given below Classes 04
Classes |
5-9 |
10-14 |
15-19 |
20-24 |
25-29 |
f |
5 |
8 |
12 |
10 |
5 |