Federal Board 2017
PHYSICS (Objective Type) Inter (Part-1)
Allowed: 15 minutes
Note: Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. The choice which you think is correct that circle in front that question with Marker or Pen ink. 'Lining or filling two or more circles 'will result in zero mat k in that question. Write the letter A, B. C or D in the column. (Write correct "option) against each question also. If there k a contradiction in the bubble and hand written answer, bubble option will be considered correct.
- The dimensions of Power are:
- [M L T-2]
- [M L T-3]
- [M2 L2 T-2]
- [M L2T-3]
- The significant figures in 34.678 are:
- 4
- 3
- 5
- 2
- Two forces are acting together on an object. The magnitude of their resultant is minimum, when the angle between the forces is:
- 120°
- 180°
- 45°
- 60°
- If the Scalar product of two vectors is 2 and the magnitude of their vector product is 2. The angle between them is:
- 30°
- 60°
- 180°
- 120°
- A car starts from rest and covers a distance of 100 m in one second with uniform acceleration. Its acceleration is:
- 100 m/s2
- 200 m/s2
- 300 m/s2
- 50 m/s2
- A ball rolls off the edge of a table. The horizontal component of the ball's velocity remains constant during its entire trajectory because:
- The net force acting on the ball is zero
- The ball is not acted upon by a force in the horizontal direction
- The ball is acted upon by a force in the horizontal direction
- The ball is acted upon by a force in the only vertical direction
- Which of the following is the example of conservative force?
- Tension in the string
- Propulsion force of rocket
- Gravitational field
- Restoring force in compressed spring
- Anybody requires_______ escape velocity, to escape from the gravitational pull of the mars.
- 2.4 km/s
- 4.3 km/s
- 5 km/s
- 10.4 km/s
- In dryer, water is pushed out of wet clothes due to:
- Abundance of centripetal force
- Lack of centripetal force
- Friction
- Retarding force
- The SI-unit of co-efficient of viscosity is:
- Kgm-1s-1
- Kgm-1 s -2
- Kgm-2 s-1
- Kgm-3s-2
- A stone of mass 16 kg is attached to a string 144 m long and is whirled in a horizontal circle. The maximum tension the string can withstand is 16 N. the maximum velocity of revolution that can be given to the stone without breaking it, will be:
- 20 ms-1
- 16 ms-1
- 14 ms-1
- 12 ms-1
- The property of fluid by which its own molecules are attracted is said to be:
- Adhesion
- Cohesion
- Viscosity
- Surface Tension
- A simple pendulum is avowed from the Earth to the Moon. How does it change the period of oscillations? (Acceleration due to gravity on moon = 1.6 ms-1)
- The period is increased by factor √6
- The period is increased by factor four
- The period is decreased by factor √6
- The period remains the same
- Which of the following conditions is best for cooking purpose?
- Isobaric
- Isochoric
- Adiabatic
- Isothermal
- What would be the efficiency of a Carnot engine operating with boiling water as one reservoir and a freezing mixture of ice and water as the other reservoir?
- 27%
- 67%
- 12%
- 100%
- Power of magnifying glasses is given by:
- ƒ+p
- 1+(d/ƒ)
- 1-(ƒ/d)
- 1+fd
-
Optically active substances are those substances which:
- Produce Polarized light
- Produce double refraction
- Rotate the plane of polarization of polarized light
- Convert a plane polarized light into circulatory polarized light
SECTION – B (Marks 21)
(Chapters 1 to 6)
Q.2 Answer any SEVEN parts. All parts carry equal marks.
- Write all possible rules for finding significant figures and significant zeros.
- Find the value of 'g' and its uncertainty using T = 2π√l/g from the following measurements made during an experiment while l=100 cm and time for 20 vibrations is 40.2s. Length was measured by a meter scale of accuracy up to 1 mm and time by stop watch of accuracy up to 0.1 second.
- A uniform sphere of weight 10N is held by a string attached to a frictionless wall so that the string makes an angle of 30° with the wall as shown in figure. Find the tension in the string and the force exerted 'on the sphere by the wall.
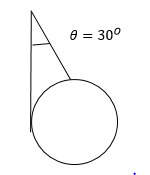
- Find the angle between two forces of equal magnitudes when the magnitude of their resultant is also equal to the magnitudes of either of these forces.
- Find the angle of projection for which its maximum height (Vertical range) achieved and horizontal range of projectile are equal?
- A truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a velocity of 21 m/s collides with stationary car weighing 1000 kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity.
- How large a force is required to accelerate an object from rest to a speed of 2x107m/s through a distance of 5cm, while the mass of electron is 9.1x10-31 kg?
- A disc and hoop start moving down from the top of an inclined plane at the same time. Which one will be moving faster on reaching the bottom and Why? (Justify your answer by using mathematical equations)
- (ix) What is the least speed at which an airplane can execute a vertical loop of 1 km radius so that there will be no tendency for the pilot to fall at the highest point.
- Water flows downhill through a closed vertical funnel. The flow speed at the top is 12 cm/s, the flow speed at the bottom is twice the speed at the top. If the funnel is 40cm- long and the pressure at the top is 1 x 105 N/m2, what is the pressure at the bottom?
SECTION-C
(Marks 21)
(Chapters 7 to 11)
Q.3 Answer any SEVEN parts. All parts carry equal marks.
- Name two characteristics of simple harmonic motion. Does Frequency depend on amplitude for harmonic oscillators? Also name some common phenomenon in which resonance plays an important role.
- Define simple pendulum. What are the drawbacks of simple pendulum? Can simple pendulum experiment be done inside a satellite?
- A pipe has length one meter, determine the frequencies of the fundamental and first two harmonics:
- If the pipe is open at its both ends
- If the pipe is closed at its both ends
- Define Doppler's Effect. And also write its few applications.
- Sketch out three differences between Interference and diffraction of light.
- State Huygens's principle. Also distinguish between a wave-front and a wavelet by graphical sketch. (Graph paper is not required)
- A glass light pipe in air will totally internally reflect a light Fay if its angle of incidence is at least 39°. What is the minimum angle for total internal reflection if pipe is in water? (The refractive Index of water is 1.33)
- Define Near Point, Resolving Power and Continuous Refraction.
- Why do we say that molar specific heat at constant pressure is greater than molar specific heat at constant Volume? (Cp > Cv)
- A steam engine has a boiler that operates at 450 k. The heat changes water to steam, which drives the piston. If the exhaust temperature at the outside air is about 300 k then calculate maximum efficiency of this steam engine?
SECTION - D
(Marks 26)
Note: Attempt any TWO questions. All questions Garry equal marks.
Q.4
- Define Absolute Potential energy. Derive relation for Absolute P.E of body having mass 'm' at distance 'r from the center of the earth.
- What is the gravitational field? Also discuss the factors on which work done by anybody in conservative field depends.
- What do you understand by the terms Critical velocity and Weightlessness.
Q.5
- What is Carnot Engine? Explain its all working steps, graphical sketch and also calculate its efficiency. Why do we say that Carnot cycle is reversible?
- Prove Boyle's law and Charles' law on the basis of kinetic theory of gases.
- Find the average speed of Oxygen molecule in the air at ST.P.
Q.6
- What is Doppler's Effect? Discuss the following cases of Doppler's effect when:
- Both Observer and are at rest
- Observer moves away towards stationary Source
- Observer moves away from stationary Source
- Source moves towards the stationary Observer
- Source moves away from the stationary Observer
- What are beats? Explain it with the help of example as well as graphically. Also mention some of its mass
- A stationary waves as unestablished in a string which is cm long and fixed at both ends. The string vibrates in four segments at a frequency of 120 Hz. Determine its wavelength and the fundamental frequency.

