Gujranwala board 2017
PHYSICSInter Part— I
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Section A
- The significant figures in 0.04060 are :
- 2
- 4
- 5
- 6
- An area of parallelogram formed by A and B two adjacent sides is given as:
- AB Sinθ
- AB Cosθ
- AB tanθ
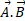
- Projection
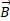 along
along 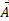 is given as:
is given as:
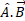
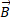
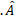
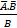
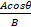
- A ball is thrown up vertically, it takes 3 sec to reach maximum height. Its initial velocity is:
- 10 ms-1
- 12.2ms-1
- 15 ms-1
- 29.4 ms-1
- A ball is thrown up with 20 ms-1 at an angle of 600 with x-axis. The horizontal velocity of the ball at the top position is
- 0 ms-1
- 10 ms-1
- 20 ms-1
- 16 ms-1
- Which one is nonrenewable source of energy?
- Hydroelectric
- Biomass
- Tides
- Oil
- If linear velocity and radius are both made to half of a body moving around a circle. Then its centripetal force becomes
- Fc
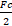
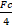
- 2Fc
- Angular momentum of a rigid body is given by:
- I(t)
- I²(t)
- I(t)²
- I²(t)²
- Venturi relation is given as:
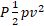
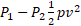
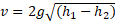
-
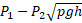
- On the average for normal healthy person diastolic pressure is:
- 120 torr
- 110 torr
- 100 torr
- 75-80 torr
- A spring of spring constant 10
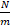 after loading the amplitude is 2m. Then the maximum P.E. is:
after loading the amplitude is 2m. Then the maximum P.E. is:
- 10J
- 20J
- 30J
- 40J
- A stretched string 4m long and it has 4 loops of stationary waves, then the wave length is:
- 1m
- 2m
- 3m
- 4m
- In which medium the speed of sound is greater?
- Oxygen
- Air
- Water
- Copper
- The light energy travels in space as waves", was firstly proposed by:
- Maxwell
- Young
- Einstein
- Huygen
- A convex lens acts as diverging lens if the object is placed at:
- F
- 2F
- Between F and 2F
- Within the 1F and 2F
- Average translational K.E. of molecules for an ideal gas is given as:
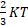
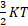
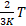
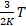
- Absolute temperature of water triplet point is:
- 0K
- 273.1.6 K
- 373.16 K
- 100 K
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q2: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature.
- Which could serve as reasonable time standards.
- Write the dimensions of force and density.
- Show that the equation E=mc² is dimensionally correct.
- Define random and systematic error.
- Name three different conditions that could make
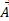 x
x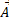 2= 0
2= 0
- Two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can their sum be zero? Explain.
- Define equal vector and null vector.
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity v and acceleration of a car are-parallel and perpendicular to one another.
- Explain what is meant by projectile motion? Derive expression for range of projectile. J'
- Define inertial and non-inertial frame of references.
- State only law of conservation of linear momentum.
Q3: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- A person holds a bag of groceries while standing still, talking to a friend. A car is stationary with its engine running. From the stand point of work, how are these two situations similar?
- In which case more work is done? When a 50 kg bag of books is lifted through 50 cm or when a 50 kg crate is pushed through 2 m across the floor with a force of 50 N?
- What is 'Aquifer"?
- Explain the difference between tangential velocity and the angular velocity.
- Write the formula which relates them.
- What is geo-stationary satellite? How many minimum number of gen stationary satellites are required for global coverage of T.V. transmission?
- Define centripetal force and centripetal acceleration.
- Does the acceleration of a simple harmonic oscillator remain constant during its motion? Is the acceleration ever zero? Explain.
- If a mass spring system is hung vertically and net into oscillations. Why does the motion eventually stop?
- Write two applications of resonance.
- What is the difference between constructive and destructive interference?
- Explain why sound travels faster in warm air than in cold air.
Q4: Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- Define wave front and ray of light.
- Describe the construction of Michelson's interferometer whit the help of diagram.
- How would you distinguish between un-polarized and plane-polarized light?
- Define near point and resolving power.
- Why would it be advantageous to use blue light with compound microscope?
- Define adiabatic process and give at least two examples of this process.
- Define Charles law on the basis of kinetic theory of gases.
- Why does the pressure of a gas in a car tyre increase when it is driven through some distance?
- Is it possible to construct a heat engine of hundred percent efficiency? Explain.
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Section C
5.
- State Newton's second law of motion in terms of momentum and prove the law of conservation of momentum.
- Find the projection of vector
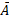 =
= 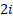 —
—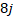 +
+ 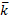 on vector
on vector 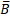 =
= 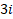 —
— 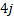 + 12k.
+ 12k.
6.
- Explain rotational kinetic energy. Prove that velocity of disc is greater than hoop. If both are rolling down from the seine height.
- An electron strikes the Screen of a cathode-ray tube with a velocity. Of 1.0 x107mS-1.
Calculate its kinetic energy. The mass of an electron is 9.1x10-31kg.
7.
- Define molar specific heats of a gas and prove that Cp—Cv= R.
- Water flows through a hose, whose internal diameter is 1 cm at a speed of 1 mS-1. What should be the diameter of the nozzle if the water is to emerge at 21 mS-1?
8.
- Derive Newton's formula for the speed of sound in air and describe the correction by Laplace in it.
- A simple pendulum is 50 cm long. What will be its frequency of vibration at a place where g = 9.8 mS-2.
9.
- Discuss in detail the experimental arrangement made by Michelson to find speed of light and determine it.
- In a double slit experiment, the 2nd order maximum occurs at 0 = 0.25°. The wave length of light used is 650 nm. Determine the slit separation.