Lahore Board 2017
PHYSICS Inter Part—1
Time Allowed: 3 HoursGroup 1
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- The triple point of water:
(A) 0 K
(B) 100K
(C) 273.16 K
(D) 373.16 K
- The time rate of change of angular displacement is called:
(A) Linear velocity
(B) Linear speed
(C) Angular speed
(D) Angular velocity
- The original source of tidal energy is:
(A) Moon
(B) Earth
(C) Sun
(D) Sean
- 2 radian = ------ :
(A) 114.6°
(B) 57.3°
(C) 75.3°
(D) 37.5°
- A stationary wave is established in a string which vibrates in four segments at a frequency of 120 Hz. Its fundamental frequency is:
(A) 15 Hz
(B) 30 Hz
(C) 60 Hz
(D) 480 Hz
- If the pressure of the gas I doubled, then the speed of sound:
(A) Is also doubled
(B) Becomes half
(C) Is not affected
(D) Increased by four times
- Venturimeter is a device used to measure:
(A) Pressure of fluid
(B) Speed of fluid
(C) Density of fluid
(D) Viscosity of fluid
- If |a+b| = |a-b| then angle between
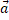 and is
and is 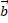 :
:
(A) 0°
(B) 45°
(C) 90°
(D) 18o°
- At constant temperature and pressure, if volume of given mass of a gas is double, then density of the gas becomes:
(A) Double
(B) 1/4 of original
(C) 1/2 of original
(D) Unchanged
- The horizontal range of a projectile at 30° with horizontal is same at an angle:
(A) 40°
(B) 45°
(C) 90°
(D) 60°
- Newton's rings arc formed as a result:
(A) Interference
(B) Dispersion
(C) Diffraction
(D) Polarization
- The horizontal component of velocity of projectile:
(A) Increase
(B) Decreases
(C) Increases or decreases
(D) Remains constant
- The distance covered during one vibration of an oscillating body in terms of amplitude ‘A’ is:
(A) A/2
(B) A
(C) 2A
(D) 4A
- The ratio of moment of interia of disc and hoops is:
(A) 1/2
(B) 1/4
(C) 3/4
(D) 1/3
- 1A layer over the central core of the Jacket is called:
(A) Jacket
(B) Plastic
(C) Cladding
(D) Rubber
- To distinguished between transvere and longitudinal wave— is used:
(A) Refraction
(B) Interference
(C) Polarization
(D) Diffraction
- 1 tera=:
(A) 1015
(B) 1018
(C) 1012
(D) 10-12
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q2: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Does a dimensional analysis give any information on constant of proportionality that may
appear in an algebraic expression? Explain
- Suggest one method of reducing the uncertainty in any timing experiment.
- How many nanosecond in one year?
- Show that the relation E = mc2 is dimensionally consistent.
- Name the two different conditions that could make
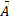 x
x 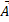 2 =
2 = 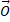 2
2
- What is the moment of a force about the point lying on the axis of rotation?
- Define position vector and resultant vector.
- Under what conditions a body can move with uniform acceleration?
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity and
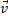 and acceleration
and acceleration 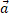 of a car:
of a car:
(a) 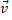 is zero but
is zero but 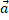 is not zero.
is not zero.
(b) 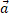 is zero but
is zero but 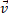 is not zero.
is not zero.
- Is the range of projectile same for both angles of projection of 30o and 60°? If your answer is yes
then prove it?
- A 20g ball hits the wall of a squash court with a constant force of 50 N. If the time of impact of
the force is 0.5sec., find the impulse?
- Explain the difference between laminar flow and turbulent below.
Q3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- When a rocket re-enters the atmosphere. its nose cone becomes very hot? Where this energy does comes from?
- A 70 kg man runs up a long flight of stairs in 4.0 sec. The vertical height of stairs in 4.5 m.
Calculate his power output in watts.
- Differentiate between geyser and aquifer.
- What is meant by INTEL SAT? At what frequencies the. INTEL SAT-IV operates?
- A body of mass 'm' is suspended from the ceiling of an elevator. If the elevator is ascending with acceleration 'a', what would be the value of 'T’ acting on the body?
- When mud flies off the tyre of moving bicycle, in what direction does it fly?
- What is driven harmonic oscillator? Give example?
- Differentiate between free and forced vibrations.
- If a mass spring system is hung vertically and set into oscillations, why does the motion eventually stop?
- What are the factors on which speed of sound in air depends?
- Which is richer in harmonics, and why:
(a) An open organ pipe.
(b) A closed organ pipe.
- Is it possible for two identical waves traveling in the same direction along a string to give rise to stationary wave?
Q4: Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- How will you increase the fringe width in Young’s double slit experiment
- In Newton's ring, Why are the fringes circular?
- How would you distinguished between un-polarized and plane polarized light?
- Write the advantage use of light as transmission carrier wave over radio wave carriers.
- If a person Was looking through a telescope at the full moon, how would the appearance of the moon be changed by covering half of the objective lens?
- Write uses of the spectrometer.
- Does entropy of a system increase or decrease due to friction?
- A thermos flask containing milk as a system is shaken rapidly. Does the temperature of milk rise?
- What is meant by reversible process? Give it examples.
SECTION-C
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q5. (a) State and prove the law of conservation of linear momentum
(b) Find the projection of vector  in the direction of the vector
in the direction of the vector 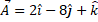
6. (a) Explain rotational kinetic energy. Find rotational kinetic energy a disc and hoop.
(b) A car of mass 800 kg travelling at 54 kmh—1 is brought to rest in 60 meters. Find the average retarding force on the car. What has happened to original kinetic energy?
7. (a) Define pressure of a gas. Prove that P =  -Na <
-Na < 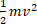 >
>
(b) A tiny water droplet of radius 0.010 cm descends through air from a high building. Calculate its terminal velocity. Givn that n for air = 19 x 10-6kgm-1s-1 and density of water p = 1000 kgm-3.
8. (a) What arc stationary waves? Describe the stationary waves produced in a stretched string and prove the their frequencies am quantized.
(b) An 8.0 kg body executes SHM with amplitude 30 cm. The restoring force is 60N when the displacement is 30 cm. Find Period and the speed when displacement is 12cm.
9. (a) What is Michelson's interferometer? Explain its construction and working.
(b) A compound microscope has lenses of focal length 1 cm and 3 cm. An object is placed 1.2 cm from the objective lens. If virtual image is formed at 25 cm from the eye, calculate the separation of lenses?
Lahore Board 2017
PHYSICS Inter Part—1
Time Allowed: 3 Hours Group 2
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- Which one is non-renewable source of energy
(A) Wind
(B) Biomass
(C) Coal
(D) Sunlight
- When a transverse wave is incident on rarer medium from a denser medium, the phase change will be
(A) 90°
(B) 60°
(C) 180°
(D) 0°
- S.I unit of angular displacement is
(A) Radian
(B) Degree
(C) Revolution
(D) Minute
- The profile of periodic waves generated by a source executing S.H.M. is represented by a
(A) Circle
(B) Sine curve
(C) Tangent curve
(D) Cosine curve
- Significant figures in 0.0004813 are:
(A) 8
(B) 7
(C) 4
(D) 3
- Density of blood is nearly equal to that of
(A) Water
(B) Iron
(C) Milk
(D) Glycerin
- For an ideal gas, the potential energy associated with its molecules is
(A) Maximum
(B) Zero
(C)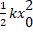
(D) 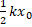
- According to Hygen's principle, each point on a wave front acts asa source of:
(A) Secondary wavelet
(B) Primary wavelet
(C) New wave front
(D) Sound
- The change in internal energy is defined as
(A) Q —W
(B) Q— T
(C) Q + P
(D) Q— P
- The resultant of 120 N and 20 N forces cannot be
(A) 141 N
(B) 100 N
(C) 101 N
(D) 130 N
- A body rotating with angular velocity of 2 radian / s and linear velocity is also 2ms-1 then radius of circle is:
(A.) 1 m
(B) 05 m
(C) 4 m
(D) 2 m
- If the speed of light in vacuum is C, then its velocity in a medium of refractive index 1.3 is:
(A) 1.3C
(B) 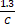
(C) 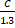
(D) C
- Total energy of a particle executing S.H.M is
(A)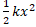
(B) 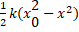
(C) 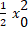
(D) 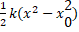
- Beats can not be recognized if difference of frequencies of two sounds is:
(A) Less than 10 Hz
(B) More than 10 Hz
(C) Less than 5 Hz
(D) Less than 7 Hz
- In the absence of external force, the change in momentum is:
(A) Zero
(B) Constant
(C) Decreasing
(D) Increasing
- Direction of angular acceleration is always along:
(A) x-axis
(B) y-axis
(C) z-axis
(D)The axis of rotation
- Height of projectile is maximum at an angle of
(A) 45°
(B) 60°
(C) 30°
(D) 90°
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q2: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Why do we find it useful to have two units for amount of substance the kilogram and the mole?
- Show that the famous Einstein equation E = me2 is dimensionally consistent.
- Explain significant figures.
- Differentiate between precision and accuracy.
- Define the term unit vector and position vector.
- Can you add zero to null vector? Explain.
- State only two conditions of equilibrium.
- Define impulse and show that how it is related to linear momentum.
- Show that the range of projectile is maximum when projectile is thrown at an angle of 45° with the horizontal.
- Derive expression of range and time of flight of projectile.
- Define elastic and inelastic collisions.
- Explain what do you understand by the term viscosity.
Q3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Write some methods to obtain solar energy.
- An object has 1J of potential energy. Explain what does it mean.
- What does negative sign show in the expression ug= -
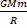
- What is moment of inertia? Explain its significance.
- State the practical use of rotational K.E. bv fly wheels.
- When mud flies off the tyre of moving bicycle, in what direction does it fly? Explain.
- How a particular station is tuned in radio?
- State the total energy of the vibrating mass and spring is constant.
- Does frequency depend on amplitude for harmonic oscillator?
- What you observe in the collective effect of dots in the form of a picture?
- Why sound travels faster in hydrogen than in oxygen.
- What feature do longitudinal waves have in common with transverse waves?
Q4: Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- How would you distinguish between un-polarized and plane-polarized lights?
- Why diffraction grating cannot be used for X-rays diffraction?
- If white light is incident on a film of irregular thickness at all possible angles, what will he the pattern of interference fringes? Explain your answer.
- A magnifying glass gives a five times enlarged image at a distance of 25 cm from the lens.
- What will be the focal length of the lens?
- What are three major components of fiber optic communication system?
- Why does the pressure of a gas in a car type increase when it is driven through some distance?
- A real heat engine is less efficient than cannot engine. Why?
- What is the similarity and difference between internal energy and gravitational P.E.?
SECTION-C
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q5. What is projectile? Derive expressions for the:
1. Height
2. Horizontal range.
(b) The magnitude of dot and cross product of two vectors are 6√3 and 6 respectively. Find the angle between the vectors.
6. (a) Define gravitational field. Prove that work in the earth's gravitational field is independent of the path followed.
(b) A body of moment of inertia 0.80 kg m2 about a fixed axis, rotates with a constant angular velocity of 100 rad s1. Calculate its angular momentum and torque to sustain this motion.
7. (a) Define Stoke's law and show that the terminal velocity is directly, proportional to square of radius of the object.
(b) 336 J of energy is required to melt 1 gm of ice at 0 °C. What is the change in entropy of 30gm of water at 0 °C as it is changed to ice at 0 °C by a refrigerator?
8. (a) What is simple pendulum? Show that its motion is simple harmonic motion. Derive an expression for its time period.
(b) A pipe has a length of 1 m. Determine the frequencies of fundamental and the first two harmonics:
1. if pipe is open at both ends.
2.if pipe is closed at one end.
9. (a) What is interference of light waves? Describe Young's double slit experiment.
(b) An astronomical telescope having magnifying power of 5 consists of two thin lenses 24
cm apart. Find the focal length of the lenses.