Lahore Board 2017
PHYSICS
Inter Part—2
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group-I
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
- S.I unit of strength of electric field is
- J/C
- C/V
- N/C
- J/N
- Which one is photo conductor:
- Copper
- Selenium
- Mercury
- Aluminium
- The numerical value of black color in carbon resistors is:
- 0
- 1
- 2
- 3
- Galvanometer can be made more sensitive if the value of factoris:
- Made large
- Made small
- Remained
- Made zero
- Controls the number of electrons
- Controls the brightness of screen
- Has negative potential
- Emits electrons
- Energy stored per unit volume in magnetic field is called:
- Electric flux
- Energy density
- Work
- Power
- Working principle of transformer is:
- Self induction
- Faraday's law
- Mutual induction
- Electromagnetic induction
- Power dissipated in pure inductor over a complete a.c cycle is:
- Large
- Small
- Infinite
- Zero
- The value of peak to peak voltage is:
- Vo
- Vo
-

- 2Vo
- At 0 K, semi conductors are:
- Conductors
- Insulators
- Perfect conductors
- Perfect insulators.
- In N-type material, minority charge carriers are:
- Free electrons
- Holes
- Protons
- Mesons
- The size of base region in a transistor is of the order of:
- 10-6 m
- 10-4 m
- 10-3
- 10-2 m
- Radiations emitted by human body at normal temperature 37°C lies in:
- X-ray region
- Infra red region
- Visible region
- Ultraviolet region
- The factorin Compton effect has the dimensions of
- Pressure
- Length
- Mass
- Momentum
- Plank's constant h is expressed as:
- J.S
- J/S
- J/S
- J.C
- The number of neutrons in the nucleus is:
- N = A - Z
- N = A + Z
- N =
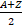
- N =
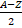
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q2: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- What are similarities between electrostatic force and gravitational force?
- What are factors upon which electric flux depend?
- The potential is constant throughout a given region of space. Is the electric field zero or non-zero in this region? Explain.
- Isnecessarily zero inside a charged rubber balloon if balloon is spherical? Assume that charge is distributed uniformly over the surface.
- A loop of wire is suspended between poles of a magnet with its plane parallel to the pole faces. What happens if a direct current is put through the coil? What happens if an alternating current is used instead?
- At a given instant, a proton moves in positive x direction in a region where there is a magnetic field in the negative z direction. What is direction of magnetic field? Will the proton continue to move in positive x direction? Explain.
- Give dimensions of permeability of free space .
- How can you use a magnetic field to separate isotopes of chemical elements?
- Show that a and have same units.
- Can an electric motor be used to drive an electric generator with output from the generator being used to operate the motor?
- If number of turns in a solenoid is doubled, keeping the other factors constant, how does the self-inductance change?
- What are the dimensions of mutual inductance?
Q3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- What are the difficulties in testing whether the filament of a lighted bulb obeys Ohm's law?
- Is the filament resistance lower or higher in a 500 w, 220 v light bulb than in a 100 w, 220 v bulb?
- Describe a circuit which will give a continuously varying potential.
- What is meant by phase of A.C quantities?
- How power is calculated in an A.C circuit? Write its formula.
- A sinusoidal current has rms value of 10A. What is the maximum or peak value?
- What are polymeric solids? Give an example.
- What is meant by hysteresis loss?
- Distinguish between intrinsic and extrinsic semiconductors.
- Write down the characteristics of operational amplifier.
- What is the net charge on an n-type or a p-type substance?
- Why charge carriers are not present in the depletion region?
Q4: Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- What are the measurements on which two observers in relative motion will always agree upon?
- Why can red light be used in a photographic dark room when developing films, but a blue or white light cannot?
- Which photon, red, green, or blue carries the most: energy and momentum?
- What is meant by a line spectrum? Explain, how line spectrum can be used for the identification of elements.
- Is energy conserved when an atom emits a photon of light?
- Describe the principle of operation of a solid state detector of ionization radiation in terms of generation and detection of charge carriers.
- What factors make a fusion reaction difficult to achieve?
- What are the basic forces of nature?
- Explain howparticles may ionize an atom without directly hitting the electrons. What is the difference in the atom of the two particles for producing ionization?
SECTION-C
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q5. (a) What is capacitor? Show that energy density for a capacitor which has electric field strength E is given by
(b) Find the current which flows in all resistances of the given circuit :
6. (a) State Amperes law and apply it to find the field due to a current carrying solenoid.
(b) An ideal step down transformer is connected to main supply of 240 V. It is desired to operate a 12 V, 30 W lamp. Find the current in the primary and the transformation ratio.
7. (a) Describe series resonance circuit. Find formula for resonance frequency and write its properties.
(b) The current flowing into the base of a transistor is 100 . Find its collector current lc, its emitter current IE and the ratio lc/IE, if the value of current gainis 100.
8. (a) Explain the photoelectric effect. What is the effect of frequency of light on photoelectric current and energy of photoelectrons?
(b) The length of a steel wire is 1.0 m and its cross-sectional area is 0.03 x 10-4m2. Calculate the work done in stretching the wire when a force of 100 N is applied within the elastic region. Young's modulus of steel is 3.0 x 1011 Nm-2.
9. (a) What are the inner shell transitions and characteristics of X-rays? Describe the production of X-rays.
(b) Find the mass defect and binding energy for tritium, if the atomic mass of tritium is 3.016049 u.