Multan Board 2017
Physics PART - II
Time: 30 Minutes
Group-I
Note: Write answers to the questions on the objective answer sheet provided. Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. Which answer you consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C and D given in front of each question with Marker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q 2. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Give similarity and difference between the Coulomb's and Gravitational Forces.
- What is 'Photoconductor?
- Why does Capacitance of a Capacitor increase when some dielectric material is inserted ' between the plates?
- How can you identify that which plate of a charged capacitor is negatively charged?
- How can you use a magnetic field to separate isotopes of chemical element'?
- At a given instant, a proton moves in the positive X-direction in a region where there is magnetic field in the negative Z-direction. What ii the direction of the Magnetic 'Force?
- What is Dead Beat Galvanometer?
- Write the formula used to convert a Galvanometer into Voltmeter
- Why the resistance of Voltmeter should high?
- A light metallic ring is released from above into a vertical bar magnet with N - pole upside. Does the current flow clockwise or anticlockwise in the ring'
- A suspended magnet is oscillating freely. in a horizontal plane. The oscillations are strongly damped when a metal plate is placed under the magnet. Explain why this occurs'?
- What are the main causes of power loss in a transformer?
Q 3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- What is the difference between Conventional Current and Electronic Current?
- What is Wheatstone Bridge? Write its Principle.
- A potential difference is applied across the ends of a Copper wire. What is the effect on the drift velocity of free electrons by increasing the potential difference and decreasing the temperature of the wire?
- What is frequency Modulation?
- How does doubling the frequency affect the reactance of an inductor and a capacitor?
- F.M. radio Waves provide a higher quality transmission of sound then A.M radio waves
- Discus briefly.
- Define Valence Band and Conduction Band.
- Define Semiconductors in terms of Energy Bands.
- Define Hysteresis Loop.
- Define Rectification and write names of its types.
- Why Ordinary Silicon Diodes do hot Mil light?
Q 4. Write short answer to any SIX (6) question
- When ultraviolet light falls on certain dyes. Visible light is emitted. Why this happen when infrared light falls on these dyes?
- Why don't we observe a Compton's effect with visible light?
- If an electron and a proton have the same de Broglie wavelength, which particle has greater speed?
- What are the advantages of lasers over ordinary light?
- What is CAT - Scanner?
- What is a radioactive tracer? Describe one application in medicine.
- Which radiation dose would deposit more energy to the body?
- 10 mGy dose to the hand or
- 1 mGy does to the entire body
- For what purpose Alcohol or Bromine is mixed with principal gas in Geiger tube?
- Is it possible that fusion of two small nuclei may occur without collision of extremely high energy?
- When ultraviolet light falls on certain dyes, visible light is emitted. Why does this not happen when infrared light falls on these dyes?
- Why don't we observe a Compton's effect with visible light?
- If an electron and a proton have the same de Broglie wavelength, which particle has greater speed?
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q 5.
- State Gauss's Law. How can you apply the Gauss's Law to calculate Electric Intensity due to an infinite sheet of charge?
- 1.0 x 107 electrons pass through a conductor in 1.0u s. Find the current M ampere flowing through the conductor. Electronic charge is 1.6 x 10-19C.
Q 6.
- Calculate torque on a current carrying coil placed in a uniform magnetic field.
- A permanent magnetic D.C motor is run by a battery of 24 V. The coil of the motor has a resistance of 2Ω . It develops a back emf of 22.5 V when driving the load at normal speed. What is the current when motor just starts up? Also find the current when motor is running at normal speed.
Q 7.
- Define phase of A.C. Also discuss the behaviour of R - C and R - L series circuits for the A.C.
- The current flowing into the base of a transistor is 100uA. Find its collector current Ic its emitter current IE and the ratio = IC/IE if the value of current gain β is 100.
Q 8.
- What is Compton Effect? Calculate Compton Wavelength.
- A 1.0 meter long Copper wire is subjected to stretching force and its length increases by, 20 cm. Calculate the tensile strain and the percent elongation which the wire, undergoes.
Q 9.
- What is Solid State Detector? Describe its principle, construction and working.
- Calculate the longest wavelength of radiation for the Paschen Series.
Multan Board 2017
Physics
PART - II
Time: 30 Minutes
Group 2
Note: Write answers to the questions on the objective answer sheet provided. Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. Which answer you consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C and D given in front of each question with Marker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
- Two parallel straight wires carrying current in opposite direction:-
- Repel each other
- They cancel out their individual magnetic effect
- Attract each other
- Have no effect upon each other
- ______is not present in A.C generator.
- Armature
- Magnet
- Slip-rings
- Commentator
- _____expressions for mutual inductance is correct.
- M =
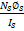
- M =
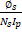
- M =
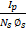
- M =
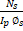
- The output voltage of an A.C generator at time t = T/4 is given by:
- V = —Vo
- V = Vo
- V=0
- V = V0/4
- The expression P = VI holds only when current and voltage are:-
- In phase
- Out of phase
- At right angle to each other
- At angle of 1200
- The substance in which atom cooperate with each other in such a way so as to exhibit a strong magnetic field is called:-
- Ferromagnetic
- Paramagnetic
- Diamagnetic
- Non-magnetic
- Logic gates can control some physical parameters like:-
- Temperature, Pressure
- Resistance, Inductance
- Capacitance, Impedance
- Current, Voltage
- The term invertor is used for:-
- NOR gam
- NAND gate
- XNOR gate
- NOT gate
- The velocity at which relativistic length of a body reduces to half of its original length is:-
- 1/2 C
- 3/2 C
- 1/√2 C
- √3/2 C
- When the K.E max of photoelectron is zero, the frequency of incident photon is_____ that of threshold frequency:-
- Less than
- Greater than
- Much greater
- Equal to
- The radiations emitted from hydrogen filled ifs mg tube can be analyzed into:-
- Band Spectrum
- Line Spectrum
- Continuous Spectrum
- Absorption Spectrum
- In Beta - deco,______ reaction takes place.
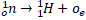
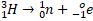
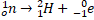
-

- The particles equal or greater in mass than that of protons is called:-
- Bearyons
- Leptons
- Mesons
- Quarks
- The drum in a photocopier is coated with a layer of:-
- Aluminum
- Silver
- Gold
- Selenium
- If a charged body is moved against the electric field it will gain:-
- Elastic Potential Energy
- Kinetic Energy
- Gravitational Energy
- Electric Potential Energy
- For Ohmic device the graph between V and I is,
- A straight line
- Curve
- Hyperbola
- Parabola
- A device used for detection of current is called:-
- Inductor
- Voltmeter
- Capacitor
- Galvanometer
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q 2. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- Define Capacitance. Also define its unit.
- Write down any two properties of Electric Field Lines.
- Describe the force or forces on u positive point charge when placed between parallel plates
- With similar and equal charge
- With opposite and equal charges
- Show that 1 eV = 1.6 x 10-19J
- Define right hand rule for determining the direction of the magnetic field.
- Define AVO meter and Ohmmeter.
- Why does the picture on T.V screen become distorted when a magnet is brought near the screen?
- Why the resistance of an ammeter should be very low?
- Write down two methods to improve the efficiency of a transformer.
- Show that ε and ΔΦ/Δt have the same units.
- Can an electric motor be used to drive an electric generator with the output from generator being used to operate the motor?
- When an electric motor, such as an electric drill, is being used, does it also act as a generator?
Q 3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- What is Wheatstone bridge? Draw its circuit diagram.
- Why does the resistance of a conductor rise with temperature?
- What is meant by the tolerance? Find the resistance of the resistor with colours Red - Violet - Orange - Silver.
- What is Choke Coil?
- What is meant by A.M and F.M?
- How does doubling the frequency affect the reactance of (a) an inductor (b) a capacitor?
- Distinguish between Crystalline and Polymeric Solids.
- What is meant by Para and Ferromagnetic substances? Give examples for each.
- Define Modulus of elasticity. Show that the units of Modulus of elasticity and stress are the same.
- The inputs of a gate are I and 0. Identify the gate if its output is (a) 0 (b) J.
- How does the motion of an electron in an - type substance differ from the motion of holes in a p - type substance?
- Why a photo diode is operated in reverse biased state?
Q 4. Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- What is NAVSTAR navigation system?
- What are the measurement on w bleb two observers in a relative motion will always agree upon?
- What are the advantages of electron microscope over an optical microscope?
- Define Ionization Energy and Ionization Potential.
- What are the reasons of unstability of heavy nuclei?
- Hydrogen atom contains one electron but its spectrum contains so many lines, explain
- Define mass deficit and binding energy.
- What are Background Radiations? Write the name of its two sources.
- What do we mean by the term Critical Mass?
- What is NAVSTAR navigation system?
- What arc the measurements on which two observers in a relative motion will always agree upon'?
- What are the advantages of electron microscope over an optical microscope?
SECTION C
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q 5.
- Define Absolute Electric Potential. Derive its relation due to a point charge.
- A Platinum wire has resistance of 10 Ω at 0°C and 20 Ω at 273° C. Find value of temperature coefficient of resistance of Platinum.
Q 6.
- Derive an expression for the energy stored in an inductor.
- What current should pass through a solenoid that is 0.5 m long with 10.000 turns of Copper wire so that it will have a magnetic field of 0.4 T?
Q 7.
- What is RLC - parallel circuit? Find the value of the resonance frequency and also write its four properties.
- The current flowing into the base of a transistor is 100 μA. Find its emitter current IE. irthe value of current gain β is 100.
Q 8.
- What is Doping? Explain formation of n - type and p - type semiconductors.