RAWALPINDI BOARD 2017
PAPER CHEMISTRY
PART-1
Time: 20 MM.
(Group-1)
(Objective Part)
Marks: 17
Note: You have four choice for each objective type question as A, B, C and D. The choice which you think is correct; fill that circle in front of that question number. Use marker or pen to fill the circles. Cutting or filling two or more circles will result in zero mark in that question.
- NH3 shows a maximum boiling point among the hydrides of with group elements due to:
(A) very small size of nitrogen
(B) lone pair of electrons present on nitrogen
(C) enhance electronegative character of nitrogen
(D) pyramidal structure of NH3
- Ionic solids are characterized by:
(A) low melting points
(B) good conductivity in solid state
(C) high vapour pressure
(D) solubility in polar solvents
- The nature of positive rays depend on:
(A) the nature of electrode
(B) the nature of discharge tube
(C) the nature of residual gas
(D) the nature of voltage supplied
- When 6d orbital is complete, the entering electron goes into:
(A) 7f
(B) 7s
(C) 7p
(D) 7d
- Which of the hydrogen halides has the highest percentage of ionic character?
(A) HC1
(B) HBr
(C) HF
(D) HI
- Which of the following species has unpaired electrons in the anti-bonding orbitals?
(A) O2 2+
(B) N22-
(C) B2
(D) F2
- If an endothermic reaction is allowed to take place very rapidly in the air the temperature of the surrounding air
(A) remains constant
(B) increase
(C) decreases
(D) remainsunehanged
- The solubility product of AgC1 is 2x10-10 mole3 dm-6. The maximum concentration of Ag+ ions in the solution is:
(A) 2.0x10-10 mole dm-3
(B) 1.41x10-5 mole dm-3
(C) 1.0x10-10 mole dm-3
(D) 4.0x10-24 mole dm-3
- An excess of aqueous silver nitrate is added to aqueous barium chloride and precipitate is removed by filtration.What are the main ions in the filtrate?
(A) Ag+and NO3 only
(B) Ag+ Ba2+ and NO3-
(C) Ba2+ and NO3- only
(D) Ba2 + NO3- and Cl-
- A solution of glucose is 10% w/v. The volume in which 1g mol of it is dissolved will be:
(A) 1 dm3
(B) 1.8 dm3
(C) 200 cm 3
(D) 900 cm3
- Stronger the oxidizing agent, greater is the:
(A) Oxidation potential
(B)reduction potential
(C) redox potential
(D) E.M.F of cell
- If the rate equation of a reaction 2A+B ------- products is, rate=k[A]2[B]1,and A is present in large excess then order of reaction is:
(A) 1
(B) 2
(C) 3
(D) 4
- The mass of one mole of electron is:
(A) 1.008 mg
(B) 0.55 mg
(C) 0.184 mg
(D) 1.673 mg
- The largest number of molecules are present in:
(A) 3.6 g of H2O
(B) 4.8 g of C2H5OH
(C) 2.8 g of CO
(D) 5.4 g of N2O5
- The comparative rates at which the solutes move in paper chromatography depend on:
(A) Size of paper
(B) Rf values of solutes
(C) Temperature of the experiment
(D) size of the chromatographic tank used
- The molar volume of CO2 is maximum at:
(A) S.T.P
(B) 127°C and 1 atm
(C) 0°C and 2 atm
(D) 273°C and 2 atm
- The deviation of a gas from ideal behavior is maximum at:
(A) -10°C and 5.0 atm
(B)-10°C and 2.0 atm
(C) 100°C and 2.0 atm
(D) 0°C and 2.0 atm
RAWALPINDI BOARD 2017
PAPER CHEMISTRY
PART-1
Time: 3:10 Hours
(Group-1)
(Subjective Part)
Marks: 83
Section-I
Q.2 Answer any Eight parts. All parts carry equal marks.
- What is function of magnetic field in mass spectrometer?
- Derive Boyle's law from kinetic molecular theory of gases.
- Define molarity and write the formula for the determination of molarity.
- State law of Mass Action. Give equilibrium constant expression Kc for the following reaction. N2 + 3H2 ↔ 2NH3
- Define filtration and crystallization.
- Why actual yield is usually less than the theoretical yield?
- Define mole with two examples.
- Why lighter gases diffuse more rapidly than heavier gases?
- Write down the four properties of a good solvent.
- Calculate pH of 10-4 mole dm-3 of Ba(OH)2 solution.
- Define atmospheric pressure. Give its two units.
- Why aqueous solution of CuSO4 is acidic in nature?
Q.3 Answer any Eight parts. All parts carry equal marks.
- Which type of particles are formed by the decay of free neutrons?
- Sodium is softer than copper but both are very good electrical conductor.
- Which ever gas is used in discharge tube, the nature of cathode rays remains the same, Why?
- Define hydrogen bonding and give one example.
- Evaporation takes place at all temperatures. Explain.
- Ionic crystals are highly brittle. Explain.
- What am the defects of Rutherford's atomic model?
- What is Mosely law?
- Aqueous solution of Na2CO3 is alkaline in nature, Why?
- What is Anodized Aluminum?
- Impure Cu can be purified by electrolytic process, Explain.
- Calculate the oxidation number of CI in the following compound Ca(C1O3)2.
Q.4 Answer any Six parts. All parts carry equal marks.
- The radioactive decay is always a first order reaction. Justify it.
- State first law of thermodynamics. Give its mathematical formula.
- What is difference between the bonding and anti-bonding molecular orbitals?
- Define dipole moment. Give its mathematical formula.
- Define Electronegativity. Give its trend in periodic table.
- What is homogeneous catalysis? Give an example.
- Define standard enthalpy of combustion with example.
- What is enzyme catalysis? Give an example.
- Define Covalent bond. Give two examples.
Section-II
NOTE: Attempt any Three questions. All questions carry equal marks.
Q 5. (a) When lime stone (CaCO3) is roasted, CaO is produced according to following equation. The actual yield of CaO is 2.5 Kg, When 4.5 Kg of limestone is roasted. What is percentage yield of this reaction?
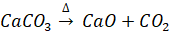
(b) Define vapour pressure of a liquid. How vapour pressure of a liquid can be measured by manometric method?
Q 6. (a) Explain Linde's method for the liquification of Gases.
(b) Derive the equation for the radius of the orbit of Hydrogen atom using Bohr's model.
Q 7. (a) State co-ordinate covalent bond with the help of two examples.
(b) State first law of thermodynamics. How does it explain that qp = qp = ΔH.
Q 8. (a) The solubility of CaF2 in water at 25°C is found to be 2.05 x10-4
mole dm-3. What is the value of Ksp at this temperature?
(b) Explain effect of concentration of reactant on rate of reaction.
Q 9. (a) Define colligative properties and discuss freezing point depression by Beckman apparatus.
(b) Give any four applications of electrolysis.