Rawalpindi Board 2017
Physics
Inter Part - I
Group 1
Note: Write answers to the questions on the objective answer sheet provided. Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. Which answer you consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C and D given in front of each question with Marker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
- The speed of sound is greater in solids than in gases due to their high
(A) Temperature
(B) Pressure
(C) Density
(D) Elasticity
- Beats cannot be heard if the difference of frequencies is more than:
(A) 10Hz
(B) 9Hz
(C) 6Hz
(D) 4Hz
- Michelson interferometer can be used to find the:
(A) Wavelength of light
(B) Wavelength of sound
(C) Velocity of sound
(D) Velocity of light
- The final image obtained by astronomical telescope is:
(A) Erect
(B) Virtual
(C) Magnified
(D) All of these
- The ratio of Cp / Cv = r for diatomic gas like air is:
(A) 1.40
(B) 1.30
(C) 1.29
(D) 1.67
- The number of spark plug needed in diesel engine is:
(A) 4
(B) 3
(C) 2
(D) 0
- The dimension of density are:
(A) [ML-2]
(B) [M2L-2]
(C) [ML-3]
(D) None of these
- If |a + b| = |a-b| x
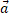 = 0, then angle between the vector is:
= 0, then angle between the vector is:
(A) 90o
(B) 180o
(C) 0o
(D) None of these
- The value of escape velocity is:
(A) 1.1Km/s
(B) 11Km/s
(C) 1.1Km/h
(D) 1.1cm/s
- If a body of mass 5kg is raised vertically through a distance of 1m, then work done is:
(A) 49J
(B) 4.9J
(C) 490J
(D) 0.49J
- The acceleration along x-axis direction in case of projectile is:
(A) Zero
(B) Equal to gravity
(C) Maximum
(D) Constant
- The SI unit of angular momentum is:
(A) Kgm2S-1
(B) Kgm2S-2
(C) Kg2mS-1
(D) KgmS-1
- Moment of inertia of rod is:
(A) I = 1/12 mL2
(B) I = 2/5 mL2
(C) I = 1/12 m2L
(D) None of these
- Height of geo-stationary orbit of the satellite above the earth is:
(A) 300Km
(B) 250Km
(C) 400Km
(D) None of these
- Bunsen Burner works on the principle of:
(A) Venturi effect
(B) Terricilli’s effect
(C) Bernoulli’s effect
(D) None of these
- Shock absorber in automobiles is a particular form of:
(A) SHM
(B) Damped oscillations
(C) Forced oscillations
(D) None of these
- Distance between two consecutive nodes is:
(A)λ/ 2
(B) λ/ 4
(C) λ
(D) 2λ
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
2- Write short answers of any eight parts from the following.
- Define radian and steradian.
- What is physical significance of dimension of physical quantity?
- How many seconds are there in one year
- Define Torque. Write its unit
- Define impulse and write its formula.
- Define: (a). Elastic collision. (b). Inelastic collision.
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which could serve as reasonable time standards.
- Can a vector have a component greater than the vector’s magnitude? Explain.
- Why can a body not rotate about its center of gravity under the action of its weight?
- Motion with constant velocity is a special case of motion with constant acceleration, is this statement true? Discuss.
- At what point or points in its path, does a projectile have its minimum speed, its maximum speed?
- How the swing is produced in a fast moving cricket ball? Explain.
3- Write short answers of any eight parts from the following.
- How can we obtain energy from Biomass?
- Define heat and explain it with an example.
- Prove that power is the dot product of force and velocity.
- What is the difference between free and forced oscillation?
- What is meant by moment of inertia? Explain briefly.
- How many minimum number of geostationary satellites are required for global coverage of
T.V transmission? Describe briefly.
- Describe two phenomenon in which resonance plays an important role.
- If a mass spring is hung vertically and set into oscillations why does the motion eventually stop?
- What is the effect of temperature on the speed of sound?
- In which case is more work done? When a 50Kg bag of books is lifted through 50cm or when a 50Kg
crate is pushed through 2m across the floor with a force of 50N.
- Why Einstein views of gravitation are preferred than Newton’s views of gravitation? Explain briefly.
- What features do longitudinal waves have in common with transverse waves?
4- Write short answers of any six parts from the following.
- How would you manage to get more orders of spectra using diffraction grating?
- Explain whether the Young’s experiment is an experiment for studying interference or diffraction effect of light.
- Why the Polaroid sunglasses are better than ordinary sunglasses?
- Explain the difference between angular magnification and resolving power of an optical instrument.
- How the light signal is transmitted through the optical fiber?
- State first law of thermodynamics and also write its mathematical form
- Is it possible to convert internal energy into mechanical energy? Explain with an example
- Can mechanical energy be converted completely into hear energy? If so give an example
-
Specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is greater than specific heat at constant volume. Why?
Section – C
Note: Answer any three questions from the following.
5. (a) What are rectangular components? Describe the method of vector addition by rectangular components.
(b) A ball is thrown horizontally from a height of 10m with a velocity of 21mS-1. How far off will it hit the
ground and with what velocity
6. (a) Show that work done in gravitational field is independent of path followed.
(b) A 1000Kg car travelling with a speed of 144Kmh-1 rounds a curve of radius 100m. Find the necessary central
force.
7. (a) What is Carnot engine? Give its four processes and derive the relation for its efficiency.
(b) The Pipe near the lower end of a large tank develop a small leak and a stream if water shoots from it. The top of water in the tank is 15m above the point of leak. With what speed does the water rush from the hole?
8. (a) What is Doppler’s effect? Explain it for two cases.
(i) When source moves towards a stationary observer.
(ii) When observer moves towards a stationary source.
(b) An 8Kg body executes SHM with an amplitude 30cm. The restoring force is 60N. Find the time period of oscillation.
9. (a) What is compound microscope? Explain its working and derive formula for its magnifying power.
(b) Blue light of wavelength 480nm illuminates a diffraction grating the second order image at an angle
Of 30O from the central image. How many lines in a centimeter of the grating have been ruled?
Rawalpindi Board 2017
Physics
Part – I Group 2
Note: Write answers to the questions on the objective answer sheet provided. Four possible answers A, B, C and D to each question are given. Which answer you consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C and D given in front of each question with Marker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
- The velocity of sound in vacuum is:
(A)Zero m/sec
(B)280mS-1
(C)332mS-1
(D)300mS-1
- When sound waves enter in different medium, the quantity that remains unchanged is:
(A)Intensity
(B)Speed
(C)Frequency
(D)Wavelength
- Longitudinal waves do not exhibit (show):
(A)Reflection
(B)Polarization
(C)Diffraction
(D)Refraction
- The light emitted from LED (Light emitting diode) has wavelength:
(A)I.3µm
(B)1.2µm
(C)I.4µm
(D)1.5µm
- Entropy is measure of:
(A)Internal energy of system
(B)Order of system
(C)Disorder of system
(D)Potential energy of system
- S.I unit of pressure of gas is:
(A)Nm-2
(B)N.m
(C)N/m
(D)N2.m
- Zero error of the instrument is a type of:
(A)Systematic error
(B)Classified error
(C)Personal error
(D)Random error
- If r = 5m and F=4N are along same direction, then torque is:
(A)20 N.m
(B)5N.m
(C)10 Nm
(D)Zero
- The distance covered by a body to time "t" starting from rest is:
(A)at2
(B)v2t
(C)
(D)
- If velocity-time graph is parallel to time axis, then acceleration of moving body will be:
(A)Maximum
(B)Positive
(C)Zero
(D) Negative
- Which one of the following force can not do any work on the particle on which it acts:
(A) Frictional force
(B) Gravitational force
(C) Electrostatic force
(D) Centripetal force
- The dimensions of power are:
(A) MLT-1
(B) ML2T-2
(C) ML2T-1
(D) ML2T-3
- When a body moves in a circle, the angle between linear velocity 'V’ and angular velocity ‘W’ is always.
(A) 90°
(B) 45°
(C) 0°
(D) 180°
- S.1 unit of moment of Inertia is:
(A) Kgm-1
(B) Kg.m2
(C) Kgm-2
(D) Kg.m
- The diver spins faster when moment of inertia becomes:
(A) smaller
(B) greater
(C) constant
(D) Zero
- The pressure will be low when speed of fluid is:
(A) low
(B) zero
(C) constant
(D) high
- The force responsible for the vibratory motion of simple pendulum is:
(A) mgcos
(B) mgsin
(C) mgsec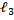
(D) mgtan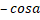
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
2- Write short answers of any eight parts from the following.
- Differentiate between elastic and inelastic collisions?
- Check the correctness of relation F=ma.
- How many years are in one second?
- Explain what do you understand by the term viscosity?
- Write down the steps for addition of vectors by rectangular component method.
- Is it possible to add a vector quantity to a scalar quantity? Explain.
- Name the three different conditions that could make
 x
x  = 0
= 0
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which could serve as reasonable time standards.
- What is the difference between uniform and variable velocity?
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity 'V’ and acceleration 'a' of a car are:
(a) Perpendicular to one another.
(b) a is zero but V is not zero.
- Derive the relation for time to reach maximum height for a projectile.
- Why do we find it useful to have two units for the amount of substance. The kilogram and the mole?
3- Write short answers of any eight parts from the following.
- Differentiate between positive and negative work.
- How are beats useful in tuning a musical instrument.
- Define resonance with one example.
- Define angular velocity give its units and demensions.
- A disc is rolling down on an inclined. Find a relation for the speed of disc at its bottom.
- How many no of geostationary satellites are required for global coverage of T.V transmission? Explain briefly.
- What is the difference between displacement and amplitude?
- A girl drops a cup from a certain height which breaks into pieces. List out all energy changes.
- Does frequency of simple harmonic oscillator depend on amplitude? Explain briefly.
- What is the effect of pressure and density on the speed of sound?
- As a result of distant explosion an observer senses a ground tremor first and then hears the explosion. Explain the time difference.
- When a rocket re-enters in atornsphere. its nose cone becomes very hot where does 's energy come from?
4- Write short answers of any Six parts from the following.
- An oil spreading over a wet footpath shows colours. Explain how does it happen?
- How would you distinguish between un-polarized lights?
- How would you manage to get more order of spectra using diffraction grating.
- Define total Internal reflection and critical angle.
- One can buy a cheap microscope for use by the children. The image seen in such microscope have coloured edges. Why is this so?
- What is heat engine? Define efficiency.
- Why is the average velocity of the molecules in a gas zero but the average of the square of velocities is not zero?
- Does entropy of a system increase or decrease due to friction'? Explain.
- Is it possible to construct a heat engine that will not expel heat in to the atmosphere? Explain.
- An oil film spreading over a wet footpath shows colours. Explain how does it happen?
- How would you distinguish between un-polarized and plane polarized lights?
- How would you manage to get more orders of spectra using diffraction grating.
Section – C
Note: Answer any three questions from the following.
5. (a) Define scalar product of two vectors and also describe its characteristics.
(b) A 1500kg car has its velocity reduced from 20mS—1 to 15mS-1 in 3 second. How large was the average retarding force?
6. (a) What are artificial satellites? Find the expression for velocity and period to put a satellite into the orbit.
(b) A child starts from rest at the top of a slide of height 4m.
(i) What is his speed at the bottom if the slide is frictionless?
(ii) If he reaches the bottom with a speed of 6m/s, what percentage of his total energy at the top of the slide is lost as a result of friction?
7. (a) State Doppler's effect and discuss the case when the observer moves towards the stationary source. Also write at least one application.
(b) A simple pendulum is 50cm long. What will be its frequency' of vibration at a place where g=9.8mS-2.
8. (a) Discuss the motion of horizontal mass spring system and also derive formula for time period, displacement and velocity.
(b) A church organ consists of pipes, each open at one end, of different lengths. The minimum length is 30mm and the longest is 4m. Calculate the frequency range of the fundamental notes.(speed of sound=340mS-1).
9. (a) Define diffraction of light. Explain diffraction of x-rays by crystal and derive Bragg's equation.
(b) A glass light pipe in air will totally internally reflect a light ray, if its angle of incidence is at least 39°. What is the minimum angle for total internal reflection if pipe is in water. (Refractive index of water=1.33)
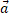 = 0, then angle between the vector is:
= 0, then angle between the vector is: 



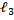
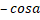
 x
x  = 0
= 0