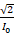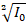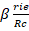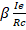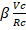Rawalpindi Board 2017
PHYSICS
(Objective Type)
Inter (Part-2)
(Group-I)
TIME: 20 Minutes
NOTE: Write answers to the questions on the objective answers sheet provided. Four possible answers A,B,C orD to each question are given. Which answer to consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C & D given in front of each question with maker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
- The electric field intensity due to an infinite sheet of charge is:
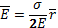
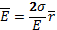
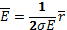
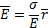
- The amount of energy equal to 1.6x1019j, is called:
- One volt
- One milli volt
- One electron volt
- One mega electron volt
- Thermo-couple converts heat energy into:
- Atomic energy
- Solar energy
- Electrical energy
- Nuclear energy
- If the number of turns becomes double but length remains same, then magnetic field in the solenoid becomes.
- Zero
- Remain same
- Half
- Double
- The SI unit of “B” is Tesla which is equal to:
- NA-2m-2‑
- NA-2m-1
- NA-1m-2
- NA-2m-1
- The emf produced by an alternating current generator is:
- NwAB sinθ
- NwAB cosθ
- NwAB sin2θ
- NwAB cos2θ
- In DC generator, split rings act as:
- Capacitor
- Commulator
- Inductor
- Resistor
- The F.M transmission frequency range from:
- 88Hz to 108Hz
- 88KHz to 108kHz
- 88MHz to 108MHz
- 88GHz to 108GHz
- When 10 V are applied to an A.C circuit, the current flowing in it is 100mA. Its impedance is:
- 100Ω
- 10Ω
- 1000Ω
- 1Ω
- The critical temperature for aluminum as super conductor is:
- 2 K
- 18 K
- 2 K
- 72 K
- Photo diode is used for detection of:
- Heat
- Magnet
- Current
- Light
- The numbers of terminal in a diode are:
- 2
- 3
- 4
- 5
- When an electron combines with a positron, we gain.
- One photon
- Three photons
- Two photons
- Four photons
- The Compton shift in wavelength will be maximum when angle of scattering is:
- 90o
- 45o
- 180o
- 30o
- For Paschen series, the value of ‘n” starts from:
- 2
- 4
- 6
- 8
- Which of the following is similar to electron:
- β–Particle
- ɑ –Particle
- Neutron
- Proton
- The element formed by radioactive decay is called:
- Father element
- Mother element
- Parent element
- Daughter element
(Subjective Part)
Section–I
2- Write short answer of any eight parts from the following.
- State guass’s Law and write is formula
- Show that 1 Volt/metre = 1 Newton\coulomb
- Define electron volt and prove that 1ev=1.6*10-19 J.
- Define capacitance of capacitor and write its formula.
- What is the function pf grid?
- Why the voltmeter should have a very high resistance?
- Define sweep voltage.
- State lenz’s law.
- Define Henry.
- Show that є and ∆∅/∆t have the same units.
- Why does the picture an a TV screen become distorted when a magnet is brought near the screen?
- Can a D.C motor be turned into a D.C generator? What change are required to be done?
3- Write short answer of any eight parts from the following.
- A potential difference is applied across the end copper wire. What is the effect on drift velocity of free electrons by decreasing the length and temperature of the wire.
- Is filament resistance lower or higher in a 500w. 220V bulb than in 100W 220V bulb.
- How many time per second will an incandescent lamp reach maximum brilliance when connected to a 50Hz source?
- In a R-L circuit, will the current lags or leads the voltage? Illustrate your answer by a vecter diagram.
- What is meant by strain energy? How can it be determined from the force-extension graph?
- Why charge carriers are not present in the depletion region?
- What is short circuit and open circuit?
- Can electrolysis take place with the help of an A.C source?
- What is semi conductor diode?
- What is meant by hysteresis loss?
- Why ordinary silicon diode do not emit light?
- What is solar cell? Give its uses.
4- Write short answers of any six parts from the following.
- Does the dialation mean the time really pass more slowly bin moving system or that it only seems to pass more slowly?
- If the following particles have same energy which has the shortest wavelength alpha particle or neutron?
- Discus the advantage and disadvantage of nuclear power compare to the use of fossil fuel generated power.
- Explain why LASER action could not occur without population inversion between atomic levels?
- Distinguish between stimulated emission and spontaneous emission.
- Find mass ‘m’ of moving objective with speed 8.8C.
- What do we mean by the term critical mass?
- Define decay constant.
- State the principle of operation of solid state detector.
Section-II
Note: Answer any three questions from the following.
- (a) Define electric potential. Drive on equation for electric potential at a point due to a point charge.
(b) 1*107 electrons pass through a conductor in 1цS.Find current in amperes flowing through conductor electronic charge is 1.6*10-19 c
- (a) What is galvanometer? How can it be converted into: (a) Ammeter (b) Voltmeter.
(b) A coil of 10 turns and 35cm2 area is in a perpendicular magnetic field of 0.5T . The coil is pulled out of the field in 1.0s.Find the induce emf in the coil as it is pulled out of the field.
- (a) How the transistor can be used as an amplifier? Explain in detail with circuit diagram and calculate its gain.
(b) What is the resonant frequency of a circuit which includes a coil of inductance 2.5H and a capacitance 40цF.
- (a) State the postulates of the special theory of relativity. Also write results of the special theory of relativity with out going out theitr mathematical derivation.
(b) A 1.25cm diameter cylinder is subjected to a load of 2500kg. Calculate the stress on the bar in mega pascals.
- (a) Write down the postulates of Bohr’s atomic model. Show that Bohr radii and their energies are quantized.
(b) A 75kg person receives a whole body radiation does of 24 m-rad, delivered by ɑ -particles for which RBE is 12 calculate:
(i) The absorbed energy in joules.
(ii) The equivalent does in rem.
Rawalpindi Board 2017
PHYSICS
(Objective Type)
Inter (Part-2)
TIME: 20 Minutes
(Group-II)
NOTE: Write answers to the questions on the objective answers sheet provided. Four possible answers A,B,C orD to each question are given. Which answer to consider correct, fill the corresponding circle A, B, C & D given in front of each question with maker or pen ink on the answer sheet provided.
- The maximum Kinetic energy of emitted photoelectrons depends upon:
(A) the intensity of incident light
(B) frequency of the incident light
(C) metal surface
(D) both frequency of incident light and metal surface
- Balmer empirical formula explains the electromagnetic radiation of any excited atom in terms of their:
(A) Energy
(B) Mass
(C) Wavelength
(D) Momentum
(A) Alcohol only
(B) Bromine
(C) Argon
(D) Neon and bromine
- How many times, the a - Particle is more massive than electron?
(A) 6332
(B) 7332
(C) 8332
(D) 9332
- If the distance between two point charges is halved, the electric intensity becomes:
(A) half
(B)  - times
- times
(C) double
(D) 4times
- The drum in photo copier is coated with layer of:
(A) Aluminium
(B) Copper
(C) Selenium
(D) Silver
- A rheostat can operate as:
(A) Amplifier
(B) Potential divider
(C) Oscillator
(D) Transformer
- Force on a moving charge in a magnetic field is given by:
(A) F =q( x )
(B) F =q( x )
(C) F =q( + )
(D) F =q( - )
- Current passing through the coil of galvanometer is:
(A) 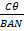
(B) 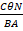
(C) 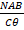
(D)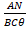
(A) VsA
(B) VsA2
(C) VsA-1
(D) V2sA-1
- If the coil is wound on an iron core, the magnetic flux through it will:
(A) Zero
(B) Increases
(C) Decreases
(D) Remain constant
- One of the source of an A.C voltage is:
(A) Motor
(B) Battery
(C) UPS
(D) Solar cell
- If I0 is the peak value of A.C current, then the root mean square (rms) value of current will be:
(A) lrms = I0/2
(B) Irms= 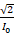
(C) 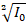
(D) 1rms=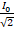
- The crystalline structure of NaCI is:
(A) Cubical
(B) Hexagonal
(C) Triangonal
(D) Tetragonal
- A diode characteristics curve is a plot between:
(A) Current and resistance
(B) Voltage and time
(C) Voltage and current
(D) Current and time
- Voltage gain of the common emitter npn-transister as an amplifier is:
(A)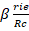
(B) 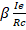
(C) 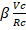
(D) 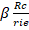
- 0.1 Kg mass will be equivalent to the energy:
(A) 5 x 108Joules
(B) 6 x 1019 Joules
(C) 9 x 1016 Joules
(D) 9 x 1015 Joules
(Subjective Part)
Section–I
2- Write short answer of any eight parts from the following.
- State Guess's Law.
- Define electric potential difference with units.
- Write down two uses of CRO.
- Why the resistance of ammeter should be low?
- What is self-induction, write down its units.
- Do electrons tend to go to region of high potential or of low potential?
- The potential is constant throughout a given region of space. Is the electrical field zero or non-zero in this region?
- Write down the formula for magnetic force on current carrying conductor in a uniform magnetic field of strength.
- Is it possible to orient a current loop in a uniform magnetic field such that the loop will not tend to rotate. Explain.
- Does the induced emf always act to decrease, the magnetic flux through a circuit?
- Four unmarked wires emerge from a transformer, what steps would you take to determine the turns ratio?
- How would you position a flat loop of wire in a changing magnetic field, so that there is no emf induced in the loop?
3- Write short answer of any eight parts from the following.
- What are the difficulties in testing whether the filament of a lighted bulb obeys Ohm's law?
- Do bends in a wire affect its electrical resistance? Explain.
- Is the filament resistance low or higher in a 500W, 220V light bulb than in a 100W, 220V bulb?
- Explain the conditions under which electromagnetic waves are produced from a source?
- How does doubling the frequency affect the reactance of a capacitor?
- Discuss the mechanism of electrical conduction by holes and electrons in a pure semiconductors element?
- What is meant by A.M and F.M?
- What are superconductors? Give examples.
- Define tensile stress and volumetric stress?
- Why a photo diode is operated in reverse biased state?
- Why is the base current in a transistor very small?
- what is the net charge on a n-type or a p-type substance?
4- Write short answers of any six parts from the following.
- What are Measurements on which two observers in relative motion will always agree upon?
- We do not notice de-Broglie wavelength for a pitched cricket ball. Explain why?
- Will higher frequency light eject greater number of electrons than low frequency light?
- Can electron in ground state of hydrogen absorb a photon of energy 13.6eV and greater than 13.6eV.
- What do you understand by background radiation? State two sources of this radiation.
- Name different quarks according to Gell-Mann and G.Zweig quark theory.
- What are advantages of laser over ordinary light?
- What do you mean by the term critical mass?
- Differentiate between Hadrons and leptons.
- What are measurements on which two observers in relative motion will always agree upon?
- We do not notice de-Broglie wavelength for a pitched cricket ball. Explain why?
- Will higher frequency light eject greater number of electrons than low frequency light?
Section–II
Note: Answer any three questions from the following.
- (a) Define electric flux. Calculate the electric flux through a sphere having a charge (+q) at its center.
(b) The resistance of an iron wire at 0°C is 1 x 104. What is the resistance at 500°C? The temperature co- efficient of resistance of iron is 5.2 x 10-3 K-1.
- (a) State and explain Faraday's law-in detail.
(b) Find the radius of an orbit of an electron moving at a rate of 2 x 107m/s in a uniform magnetic field of 1.2 x 10-3 T.
- (a) What is operational amplifier? Describe operational amplifier as non inverting amplifier. Calculate its gain.
(b) Find the value of the current and inductive reactance, when A.C voltage of 220V at 50Hz is passed through an inductor of 10H.
- (a) What is photoelectric effect? How its different results were successfully explained by Einstein?
(b) A 1.25cm diameter cylinder is subjected to the load of 3000Kg. Calculate the stress on the cylinder in mega pascals.
- (a) Define LASER and explain population inversion and laser action.
(b) The half life of Sris 9.70 hours. Find its decay constant.
- times