Sahiwal Board 2017
PHYSICS
Inter Part-1
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group 1
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- A wheel of radius 2m turns through an angle of 57.3°, it lays out a tangential distance of:
(A) 2 m
(B) 4 m
(C) 57.3 m
(D) 114.6 m
- The weight of a body at the centre of earth is:
(A) maximum
(B) minimum
(C) zero
(D) infinite
- Kilowatt hour is the unit of
(A) work
(B) force
(C) power
(D) momentum
- For a typical rocket, how much of mass of rocket is in the form of fuel?
(A) 60%
(B) 50%
(C) 80%
(D) 90%
- 5. For which pair of angles the range of projectile are equal:
(A) 70°, 20°
(B) 20°,30°
(C) 60°,40°
(D) 50°,10°
- lf
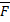 = 2
= 2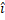 + 3
+ 3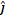 N and
N and 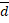 = 4
= 4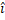 +34
+34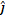 m then the work done will be:
m then the work done will be:
(A) 13 J
(B) 18 J
(C) 20 J
(D) 24 J
- One giga is equal to:
(A) 109
(B) 10-9
(C) 1012
(D) 10-12
- The difference between Cp and Cv is equal to:
(A) Plank's constant
(B) general gas constant
(C) Molar gas constant
(D) Boltzman constant
- No spark plug is needed in the
(A) petrol engine
(B) gas engine
(C) diesel engine
(D) water engine
- If focal length of objective and eye piece is 0.5 m and 10 cm respectively then magnifying power of telescope will be:
(A) 5
(B) 0.5
(C) 10
(D) 20
- Using a graded index fiber, the time difference is reduced to about:
(A) 33 ns per 100km
(B) 33 ns per km
(C) 1 ns per km
(D) 1ns per 100 km
- Star moving away from earth shows:
(A) Blue shift
(B) Red shift
(C) Doppler's shift
(D) Frequency shift
- Beats detectable eaily up to frequency difference between two sound is
(A) 2 Hz
(B) 6Hz
(C) 10 Hz
(D) 32 Hz
- The louder the sound, the greater will be its:
(A) speed
(B) frequency
(C) Amplitude
(D) wavelength
- If the time period of simple pendulum is 2 second, its frequency will be
(A) 1 Hz
(B) 0.5 Hz
(C) 1.5 Hz
(D) 2 Hz
- SI unit of coefficient of viscosity is:
(A) Kg m-1s-1
(B) Kg m-1s
(C) kg ms-1
(D)Kg-1m-1s-1
- A mass of 1 Kg is freely falling. The force of gravity is:
(A) 1N
(B) 9.8N
(C) 0.5N
(D) Zero
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
Q2: Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- What are base units and derived units? Give its examples.
- Define light year. How many meters are there in one light year(speed of light= 3 x 108 ms-1)
- Slow that the famous "Einstein Equation" E= mc² is dimensionally consistent.
- Write the dimensions of
- Define torque. Write down its S.I unit.
- under what circumstances would a vector have components that equal in magnitude?
- Name the three different conditions that could make
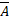 1 X
1 X 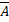 2 = 0
2 = 0
- Find the angle of projection of projectile for which its maximum height and horizontal range are equal.
- Derive expression for the range of projectile and show that the range of projectile is maximum when projectile is thrown at an angle of 450 with the horizontal.
- Can the velocity of an object reverse the direction when acceleration is constant? If so, give an example.
- What is ballistic flight and ballistic missile?
- Why fog droplets appear to be suspended in air?
Q3. Write short answers to any EIGHT (8) questions.
- An object has 1J of potential energy. Explain what does it mean?
- State work energy principle. Give its one example.
- What is Salters duck?
- Show that orbital angular momentum. Lo = m v r.
- What type of energies are possessed by a hoop moving down frictionless inclined plane?
- What will be the effect on moment of inertia of a cylinder of about its axis if its diameter is doubled.
- If a mass spring system is hung vertically and set into oscillations, why does the motion eventually stop?
- Describe the condition under which a vibrating body resonates with another body.
- What will be the Potential Energy of a mass attached to a spring at amplitude of 5 cm, if its spring constant is 10Nm-1?
- Why does sound travel faster in solids than in gases?
- Why “stationary waves” are called standing waves?
- What are the conditions for constructive and destructive interference of waves?
Q4: Write short answers to any SIX (6) questions.
- How would you distinguish un-polarization and plane – polarized lights?
- State Huygens’s principle.
- Under what conditions two are more sources of light behave as coherent sources?
- How the light signal is transmitted through the optical fibre?
- Find magnifying power of convex lens of 25 cm focal length acts as a magnifying glass.
- Specific heat of a gas at constant pressure is greater than specific heat at constant volume.
- State Comet's theorem.
- Give an example of a natural process that involves an increase in entropy.
- What do you mean by triple point of water?
SECTION-C
Note: Attempt any THREE questions.
Q5. (a) Describe addition of two vectors 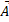 and
and 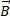 by using rectangular components.
by using rectangular components.
(b) A truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a speed of 21ms-1 collides with stationary car weighing 1000 kg. The truck and the car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity.
Q6. (a) What is conservative field? Show that work done in gravitational field by gravitational force is independent of path followed.
(b) A gramophone record turn table accelerates from rest to an angular velocity of 45 rev. min-1 in 1.6 seconds. Find average angular acceleration.
Q7. (a) Explain four stroke petrol engine in detail. What is the efficiency of a diesel engine?
(b) What gauge pressure is required in the city mains for a stream for a fire hose connected to the mains to reach a vertical height of 15 m.
Q8. (a) What is Doppler's effect? Discuss its four cases.
(b) A 100 g body hung on a spring elongates the spring by 4.0 cm. When a certain object is hung on the spring and set vibrating, its period is 0.568 s. What is the mass of the object pulling the spring?
Q9. (a) What is spectrometer? Describe its construction, working and uses.
(b) X-rays of wavelength 0.150 nm are observed to undergo a first order reflection at a Bragg angle of 13.3° from a quartz (SiO2) crystal. What is the inter planar spacing of the reflecting planes in the crystal?