Sargodha board 2017
PHYSICSInter Part—1
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group 1
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- The Dimensions of the relation
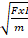 are equal to the dimensions of
are equal to the dimensions of
- Force
- Momentum
- Acceleration
- Velocity
- A Cosθ
- B Sinθ
- A Sinθ
- B Cosθ
- For a rocket, the change in momentum per second of the ejecting gases equal
- Acceleration of the rocket
- Momentum of the rocket
- Velocity of the rocket
- Thrust acting on rocket
- The acceleration of a projectile along x-axis is
- Zero
- Increases
- Decreases
- Equal to ‘R'
- Which of the following is non conservative force
- Frictional force
- Gravitational force
- Electric force
- Elastic Restoring force
- The unit of rotational K.E is
- rad/sec
- JS
- J
- Kg m2
- Which of the following is not directed alone the fixed axis of rotation?
- Angular Displacement
- Angular Momentum
- Centripetal Acceleration
- Angular Acceleration
- Choose the quantity which plays the same role in Angular motion as that of mass to Linear motion
- Angular acceleration
- Torque
- Moment of Inertia
- Angular momentum
- The instrument which detects the instant at which the external pressure becomes equal to the systolic pressure is called?
- Manometer
- Sphygmomanometer
- Barometer
- Stethoscope
- Oscillation of shock absorber of a car is a practical example of
- Simple Harmonic motion
- Forced oscillations
- Damped oscillations
- Undamped oscillations
- The wave length of a transverse wave travelling with speed '
 ' having frequency'
' having frequency' '
'
- ƒ/v
- vƒ
- v/ƒ
- ƒ/v2
- Beats eon be hear when difference of frequency is not more than
- 8 Hz
- 10 Hz
- 12 Hz
- 16 Hz
- In a organ pipe which is open at one end and closed at other, the frequency of fundamental note is
- ƒ1 = v/4
- ƒ1 = 4l/v
- ƒ1 = v/2l
- ƒ1 = 2l/v
- If ‘N’ is number of lines ruled on the grating having length 'L’ then grating element ‘d’ is given by
- N/L
- 2N/L
- L/N
- N/2L
- Using a graded Index Fibre, the time difference is reduced to about
- 15
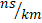
- 10
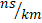
- 5
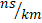
- 1
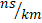
- Which one is true for Isothermal process
- Q=W
- Q=0
- W=0
- W-=ΔU
- The coherency of diesel Engine is about
- 25% to 30%
- 35 % to 40 %
- 40 % to 50 %
- 50 % to 60 %
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
2. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- Name several repetitive phenomenon occurring in nature which could serve as reasonable time standards.
- Mass is a form of enemy. How much energy is equivalent to one kg mass, according to Einstein's theory
- Find the dimensions of coefficient of viscosity η in the relation of Stoke's law F = 6πηrv
- Define precision. Which instrument can measure precise value meter rod or vernier calipers?
- Two vectors have unequal magnitudes. Can their sum be zero? Explain.
- Can a body rotate about its center of gravity under the action of its weight?
- State first and second conditions of equilibrium in terms of linear and angular acceleration. (silt) Can the velocity of an object reverse the direction when acceleration is constant? If so, give an example.
- Explain the circumstances in which the velocity "v" and acceleration "a" of a car are
- Parallel
- Perpendicular to each other.
- What is the significance of slope of velocity-time graph?
- Water is projected from two rubber pipes at the same speed v from one at 30o and from other 60o why are the ranges equal?
- Explain the difference between laminar flow and turbulent flow?
3. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- A stone is dropped from a height of 10 m vertically downward. What energy Changes are involved?
- What do you mean by variable force Give two examples
- In which case is more work done? When a 50 kg bag is lifted through 50 cm or a 50 kg crate is pushed through 2 m across the floor with a force of 50 N?
- Banked tracks are needed for rums on Highway.
- Why? Does the Coasting rotating system slow dorm as some malarial object is added to the system daring rotation?
- When mud flies off the tyre of a moving bicycle, in what direction does it fly? Explain.
- Can we realize an ideal simple pendulum? Explain.
- Explain one example of electrical resonance.
- What happens to the period of a simple pendulum if its length is doubled?
- Find the temperature of air if the velocity of sound is 340 ms-1 at that temperature.
- Why does sound navel faster in solids than in gases?
- What features do longitudinal waves have in common with transverse waves?
4. Answer briefly any six parts from the followings.
- Explain whether the Young's experiment is an experiment for studying interference or diffraction effect of light
- Can visible light produce interference fringes? Explain.
- Define wave-front and diffraction of light.
- Define critical angle and total internal reflection.
- Explain the difference between angular magnification and retaining power of an optical instrument
- How the power is lost in optical fiber through dispersion? Explain.
- State any four postulates of Kinetic Theory of gases.
- A thermos flask containing milk as a system is shaken rapidly. Does the temperature of the milk rise? Explain
- Derive Charles' Late from Kinetic Theory of gases.
SECTION C
Note: .Attempt any three questions
Q 5:
- Define components of a vector Describe the addition of vectors by rectangular components.
- A truck weighing 2500 kg and moving with a velocity of 21 ms-1 Collides with a stationary, Car weighing 1000 kg. The truck and the Car move together after the impact. Calculate their common velocity
Q 6:
- Define geo-synchronous satellite. Derive the relation for radius of a satellite whose orbital mahouts synchronized Olathe rotator of the Earth. Also find the height of such satellite above the surface of Earth
- How large a force is required to accelerate an electron (m = 9.10 10-31 kg) from rest to b speed of 2.0.107 ms-1 through a distance of 5.0 cm?
Q 7:
- On the basis of Kinetic theory of gases, prove that pressure of a gas is directly proportional average K.E. of gas molecules.
- Water is flowing smoothly through a closed pipe system. At one point the speed of water is 3 ms-1, while another point 3 m higher, the speed is 4 ms-1. If the pressure is 80 KPa at the lower point what is the pressure at the upper point.
Q 8:
- Show that the motion of the projection of a particle moving around a circle is SHM and derive the relation for its instantaneous velocity.
- A pipe has a length of 1m. Determine frequencies of the fundamental and the firm two harmonics if the pipe is closed at one end. Speed of sound is 340 ms-1
Q 9:
- Describe and explain the diffraction of X-rays by crystals and obtain Bragg's equation
- An Astronomical telescope having magnifying power of 5 consists of two thin lenses 24cm apart. Find the focal lengths of the tenses.
Sargodha board 2017
PHYSICSInter
Part—1
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group 2
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- The absolute uncertainty for vernier calipers of v.c = 0.01 cm is
- 0.1 mm
- 0.01 m
- 0.001 cm
- 0.001 mm
- The Angle of
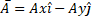 with X-axis will be in between
with X-axis will be in between
- 0oand 90°
- 90° and 180o
- 180° and 270°
- 270° and 360o
- Area under velocity-time graph represents
- Force
- Distance
- Acceleration
- Speed
- A typical rocket consumes about 10000 Kgs-1of fuel and ejects the burnt gas at speeds of over
- 2000 ms-1
- 3000 ms-1
- 4000 ms-1
- 5000 ms-1
- Biomass is converted into fuel by
- Evaporation
- Fermentation
- Reflection
- Scattering
- The rotational kinetic energy of a solid sphere is
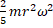
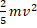
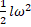
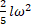
- The light from stars can be focused by their
- Mass
- Distance
- Radius
- Gravity
- The product of rotational inertia and angular velocity “ω” is equal to
- Torque
- Linear momentum
- Angular momentum
- Force
- The concentration of red blood cells in the blood is nearly
- 40%
- 50%
- 60%
- 25%
- By increasing doe mass of a simple pendulum its period
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains same
- Become zero
- The distance between a compression and its adjacent rarefaction is
- π/2
- π
- 2π
- π/4
- Frequency range of bearing of cats is
- 20 — 20000 Hz
- 10 — 10000 H.
- 60 —20000 Hz
- 60 — 70000 Hz
- The waves used in radar speed trap are
- Longitudinal
- Sound waves
- Microwaves
- Matter waves
- Fringe spacing is equal to
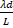
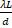
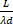
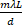
- The units of magnifying power of microscope or telescope are
- Meter
- m-1
- Dipole
- No unit
- The value of Boltzmann constant "K" is
- 1.38x10-15JK-1
- 138 x 10-23 JK-1
- 13.8. 10-23 JK-1
- 8.314 JK-1
- In adiabatic process First law of thermodynamics reduces to
- Q = W
- Q = Δ U
- W = — ΔU
- W = 0
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
2. Answer briefly any eight parts from the followings.
- Distinguish between base wits and derived units.
- Derive the dimensions of coefficient of viscosity and pressure.
- Differentiate between precision and accuracy.
- Calculate the number of swords and nanoseconds in one year
- A picture is suspended from a wall by two strings. Show by diagram the configuration of the strings for which the tension in strings will be minimum
- Is it possible to add scalars and vectors explain briefly?
- Show by diagram that vector addition commutative
- State Newton’s second law of motion and define the unit of force.
- Define average and instantaneous velocity of a moving body. Under what circumstances these velocities are equal.
- A ball is thrown vertically up with 20 ms-1. It returns on ground after 4 sec show this meson with velocity time graph.
- What is the effect on the speed of a fighter plane chasing another when it opens fire.What happens to the speed of pursued plane when it returns the fire.
- Explain briefly, one working of a carburetor in the engine of motor car using by Bernoules principle.
3. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- An object has one Joule of potential energy. Explain what does it mean?
- A girl drops a cup from a certain height, which breaks into pieces. What energy changes are involved?
- Derive w expression of power in terms of force and velocity.
- Explain conservation of direction of angular momentum
- Explain the difference between tangential velocity and the angular velocity.
- What should he the minimum velocity, for a satellite to orbit close to the Earth around it?
- Dose the acceleration of a simple harmonic motion remains constant during its moron, Is the acceleration event zero? Explain
- What happens to the period of the simple pendulum if the length is halved and mass of bob is doubled?
- Why waves of 2410 MHz frequency is necessary for heating and cooking of food in micro wave oven?
- Explain why energy remains "Standing” in the medium between nodes?
4. Answer briefly any SIX parts from the followings:
- How would you manage to get of spectra using a diffraction grating?
- What is difference between interference diffraction?
- An oil film spreading over a wet footpath shows colours. Explain how does it happen?
- How the power is lost in optical fiber through dispersion? Explain.
- What is the function of collimator in a spectrometer?
- Why does the pressure of a gas in a cm tyre increase when it is driven through some distance?
- Write four postulates of kinetic theory of gasses
- Does entropy of a system increase or decrease due to friction?
- State second law of thermodynamics in teens of entropy,
SECTION C
Note: Attempt any three questions.
Q 5:
- What is Elastic Collision in case of elastic Collision of two bodies in one dimension? Find their velocities after collision
- Two forces of magnitude of 10 N and 20 N act on a body in directions melting angle 30o and 60o respectively with x-axis. Find the resultant form and direction.
Q 6:
- Define Gravitational field. Prove that work done in a gravitational field is independent of path followed.
- An electric fan rotating at 3 rev.s-1 is switched off It comes to rest In 18 sec. Assuming deceleration to be uniform, find Its value. How many revolutions did it cum before corning to rest?
Q 7:
- Define molar specific heat of a gas at constant pressure. Prove Mat CF - CV =R
- What Gauge pressure is required in the city mains for a stream from a fire hose connected to the mains to reach a vertical height of 15 m?
Q 8:
- Define simple pendulum. Prove that the oscillation of simple pendulum is simple harmonic motion. Derive formula for its time period.
- Find the temperature at which the velocity of sound in air is two times its velocity at 10oC
Q 9:
- Explain Young's double slit experiment and determine the relation for linear distance on the screen between adjacent bright fringes.
- A compound microscope has lenses of focal length 1.0 cm and 3.0 cm. An object is placed 1.2 cm from the object lens. If a virtual Image 4 formed 25 on (torn the eye, calculate the separation of the lenses.