Sargodha board 2017
PHYSICS
Inter Part—II
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group 1
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- In SI units, the value of permittivity of free space () is
- 9x109Nm2C-2
- 9.10-9C2N-1m-2
- 8.85.1012C2N-1m-2
- 8.85x1012C2N-1m-2
- The direction of field lines around an isolated negative charge'- q' is
- Radially inward
- Radially outward
- Elliptical
- Circular
- The current which flows from a point at higher potential to a point at lower potential is called
- Electric current
- Conventional current
- Either of these
- None of above
- A current carrying conductor experiences maximum magnetic force in a uniform magnetic field when it is placed
- Perpendicular to field
- Parallel to field
- At an angle of 60° to the field
- At an angle of 180° to the field
- In current carrying long solenoid the magnetic field produced does not depend upon.
- The radius of solenoid
- Number of turns per unit length
- Current flowing through solenoid
- All of above
- When a conductor moves across a magnetic field. an emf is set up, this end is called
- Variable emf
- Constant emf
- Back emf
- Induced emf
- The motional end depends upon the
- Length of conductor
- Speed of conductor
- Strength of magnet
- All of these
- The phase of AC at positive peak from origin is
- 3π/2
- π/2
- π/4
- π
- In pure capacitor AC circuit, the current and charge are
- In phase
- Out of phase
- Parallel to each other
- None of above
- A solid having regular arrangement of molecules throughout its structure is called
- Amorphous solid
- Polymeric solid
- Glassy solid
- Crystalline solid
- The value of potential banter for silicon at mom temperature is
- 0.7V
- 0.5V
- 0.3 V
- 0.9 V
- The central region of transistor is known as
- Emitter
- Base
- Collector
- Depletion region
- The theory of relativity wee proposed by
- Newton
- Maxwell
- Compton
- Einstein
- The mass of object will be doubled at speed.
- 2.6x 108m/s
- 1.6.108m/s
- 3.6x108m/s
- 0.6x108m/s
- X-ray diffraction reveals that these are
- Panicle type
- Wave type
- Both wave and particle
- None of above
- 1.67x 10-21kg
- 1.6 x 10-19
- 1.67 x 10-31
- 9.1 x 10-31kg
- When a nucleus emits alpha panicle. its atomic mass decreases by
- 1
- 2
- 3
- 4
SUBJECTIVE PART
SECTION B
2. Answer briefly any EIGHT parts from the followings:-
- Define electric potential and give its S.I unit.
- What are the similarities and difference between electric and gravitational forces?
- If a point charge 'q' of mass m is released in a non-uniform electric field lines pointing in the same direction, will it make a rectilinear motion?
- Electric lines of force never cross why?
- Define Testa and write its formula.
- What do you know about the sensitivity of galvanometer
- Why the voltmeter should have a one high resistance
- Why the picture on a TV Screen does becomes distorted when a magnet is brought near the screen.
- On which factors the mutual inductance of the two coils depends?
- State Faraday's Law of electromagnetic induction. Write its mathematical form.
- In a transformer, there is no transfer of charge from the primary ha the secondary coil, How is then the power transferred
- Can a D.C motor be turned into a D.C generator? What changes are required to be done?
3. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- Why does the resistance of a conductor rise with temperature?
- Describe a circuit which gives a continuously varying potential.
- How the heating effect produced when current flows through the conductor?
- Ina R-L circuit will the current lag or lead the voltage? Illustrate your answer by a vector diagram.
- How the reception of a particular radio station is selected on your radio station
- Why a transformer cannot work on D.C input supply? Comment.
- Define modulus of elasticity. Show that unit of modulus of elasticity and stress are same.
- Distinguish between a valence and conduction band.
- Define coercivity of a material.
- Why charges are not present in the depletion region?
- Why a photo-diode is operated in reverse biased? Comment.
- Draw the symbolic diagram of NOT gate and also mite its truth table.
4. Answer briefly any six parts from the following:
- Define Compton Effect.
- Which photo red, green, or blue carries the most (a) energy and (b) momentum?
- Will bright light eject more elections from a metal surface than dimmer light of the same colour?
- Write two properties of X-rays.
- What do we mean when we say that the atom is excited?
- Define mass defect and binding energy.
- Define half-life of a radioactive element and write its formula.
- A particle which produces more ionization is less penetrating. Why?
- How can radioactivity help in the treatment of cancer?
SECTION C
Note: Attempt any three questions.
5.
- Define capacitor and capacitance. Derive the formula for energy stored in a capacitor.
- The resistance of an iron wire at 0°C is lx 104 . What is the resistance at 500oC , if the temperature coefficient of resistance of iron is 5.2 x 10-3K-1.
6.
- Define Motional EMF. Derive a relation for Motional EMF?'
- A power line 10.0 m high carrel a current 200 A. Find the magnetic field of the wire at the ground
7.
- Define stress and strain. Write a note on Young's, Bulk and shear mules.
- An electron is placed in a box about the site of an atom that is 'about 1.0x10-10m. What is the velocity of electrons?
8.
- What is Radioactivity? Discuss the emission of particle, particle and -radiation from a radioactive nuclei.
- Calculate the longest wavelength of radiation for the Paschen series.
9.
-
Whet are electromagnetic waves? Discuss principle of generation, Transmission and reception of electromagnetic waves.
- Calculate the gain of non-inverting amplifier shown in fig.

Sargodha board 2017
PHYSICS
Inter Part—II
Time Allowed: 3 Hours
Group 2
Note:-Three are THREE sections in this paper i.e. Section A. B and C. Attempt Section-A on the same paper and return it to the superintendent within the given time. No marks will be awarded for Cutting, Erasing or Overwriting. Marks of Identification will lead to UFM case, Mobile Phone etc. are not allowed in the examination hall.
Q1. Write the correct option i.e. A, B, C or D in the empty, box provided opposite to each part.
- Energy stored in the capacitor with dielectric is
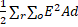
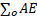
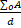
-
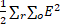
- The photo copying process is called
- Photography
- Scarfing
- Xerography
- Holography
- Resistance tolerance of silver band is
- 10%
- 6%
- 7%
- 5%
- High resistance in voltmeter is given by
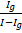
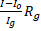
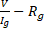
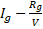
- Magnetic lines of force are
- Imaginary
- Real
- Perpendicular
- In phase with electric lines of force
- Induced emf of ac. Generators
- VBLsinθ
- IBLsinθ
- NWABsinθ
- NIABcosα
- AS motor speeds up, back emf
- Increases
- Decreases
- Remains same
- Becomes zero
- is low for low frequency f, but is
- Zero
- Low
- High
- Same as
- Power dissipation M a pure inductive circuit over a complete cycle is
- Large
- Small
- Infinite
- Tern
- Soft magnetic material is
- Iron
- Sodium
- Steel
- Copper
- The circuit which compares the two voltages is
- LDR
- Sensor
- Comparator
- Logic gate
- The inverse current in a diode is due to
- Minority charge carriers
- Holm
- Majority charge carriers
- Electrons
- The minimum energy required to create pair production is
- 1.02 Key
- 1.02 Mev
- 1.02 ev
- 1.02J
- Momentum of moving photon is given by
- h/λ
- hc/λ
- hƒ
- hλ/c
- Second postulate of Bohr's atomic model is
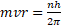
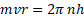
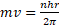
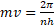
- In nuclear radiations. track of is
- Thin
- Discontinuous
- Erratic
- Continuous
- Iodine- 131 is used for the treatment of
- Bones
- Eyes
- Thyroid glands
- Lungs
2. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- Distinguish between conductor and photo-conductor.
- A pergola carrying a charge of 2e fells through a potential difference of 3.0 V. calculate the energy acquired by it.
- The potential is constant throughout a given region of space. Is, the electrical field zero or non-zero in this region? Explain.
- How can you identify that which plate of a capacitor is positively charged?
- Why the voltmeter should have a very high resistance?
- Describe the change in magnetic hold inside a solenoid carrying a steady current, if the number of turns is doubled, but length remains constant.
- How can you use a magnetic field to separate isotopes of chemical element?
- Can en electron at rest be in motion with a magnet? Describe.
- Define mutual inductance and write its unit.
- Show that and have the same units.
- When the primary of a transformer is connected to a.c mains the current in it
(a) is very small if the secondary circuit is open, but
(b) increases when the secondary is closed-explain these facts.
- Can a D.C motor be turned into D.C-generator? What changes are required to be done?
3. Answer briefly any Eight parts from the followings:-
- State Kirchhoff’s point Rule and write it in mathematical form.
- Do bends in e wire affect its electrical resistance Explain
- Why does the resistance of a conductor rise with temperature
- Give advantages and disadvantages of F.M Over A.M
- A Sinusoidal current has rms value of 10 A. What is the maximum or peak value?
- How many limes per second will an Incandescent lamp reach maximum brilliance when connected to 50 Hz source?
- Define (a) crystal lattice (b) unit cell.
- Define Bulk modulus and give its units.
- What are ductile materials: Gives its two examples.
- Define the term logic gate. Write names of fundamental gates.
- Name three basic characteristics of op-Amp. Also give their approximate values.
- Why is the base current in a transistor very small? Explain.
4. Answer briefly any, Six parts from the followings:-
- As a solid is heated and begins to glow, why does it first appears red?
- Define photoelectric effect and pair production.
- What advantages an electron microscope has over an optical microscope?
- Write down any two uses of laser in medicine
- What do we' mean when we say that the atom is excited?
- Define radioactivity and half-life.
- A particle which produces more ionization is less penetrating. Why?
- What do you understand by background radiations? State Boor sources of this radiation.
- Discuss the advantages and disadvantages of fusion power from the point Of safety, pollution and resources.
SECTION C
Note: Attempt any three questions.
Q.5.
- Define electric potential at a point due to point charge and derive mathematical expression for it
- The resistance of an iron wire at 0°C is 1x104 . What is resistance at 500°C if the temperature co-efficient of resistance of iron is 5.2 x 10-3K-1?
Q.6.
- State and explain the phenomenon of mutual induction. Also define Henry.
- Find the radius of an orbit plan of an electron moving at rate of 2.0 x 107ms-1 in a uniform magnetic field of 1.20x10-3T
Q.7.
- What is meant by rectification? Explain the action of a semiconductor diode as half wave rectifier.
- A sinusoidal AC has a maximum value of 15 A. What are its rms values? if the time is recorded from the instant the current is zero end is becoming positive, what is the instantaneous values of Current after I / 300 s, given the frequency is 50 Hz?
Q.8.
- What is photoelectric effect? How Einstein explain it on the basis of quantum theory?
- What strew would cause a wire to increase in length by 0.01% if the Young's modulus of the wire is 12 x 1010 Pa. what force would produce this stress if the diameter of the wire is 0.56 mm?
Q.9.
- What are X-rays? Describe the production of X-rays.
- Find the mass detect and Re binding energy for tritium, if the atomic mass of tritium is 3.016049U.
